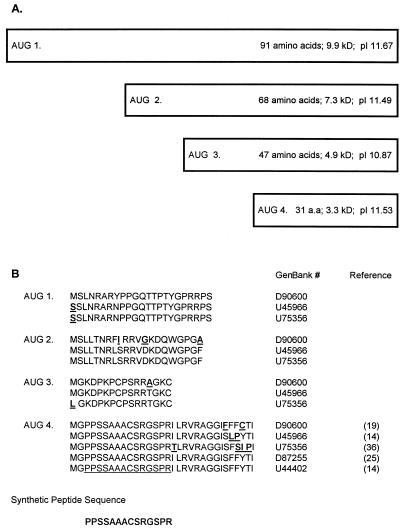
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of potential HGV core proteins. The boxes represent the potential amino termini of the HGV polyprotein. All AUGs shown are in frame with the putative E1 protein for one HGV isolate (GenBank accession no. D90600) (19). The predicted number of amino acids, molecular mass, and pI are noted for each protein. Predicted molecular mass and pI were calculated by the Network Scientific Toolkit (DNA and Protein Analysis Toolkit, provided by The Rockefeller University). (B) The translated amino acid sequence starting with each AUG until the next AUG for one HGV isolate is shown on the top line (19). This sequence is compared with those of four additional HGV isolates below. The GenBank accession number and reference are shown in the right column. Nucleotide insertions created frameshifts for isolates D87255 and U44402 between the third and fourth AUGs of D90600. If these frameshifts did not occur, there would be greater than 90% amino acid homology for the 91-amino-acid “core” protein. The synthetic peptide sequence utilized in the immunoassay is shown at the bottom of the figure.