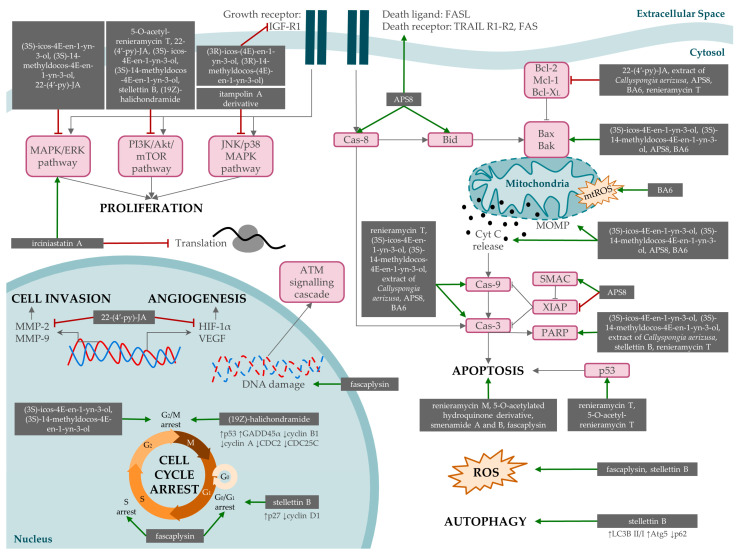
Figure 6.
Mechanisms of action by which compounds derived from marine sponges exert their effect on lung cancer lines. Most of the mechanisms are related to proliferation, cell invasion, angiogenesis, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, ROS production, and autophagy. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3K; protein kinase B, Akt; serine/threonine-protein kinase, mTOR; mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK; extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK; c-Jun N-terminal kinase, JNK; insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, IGF-R1; Fas cell surface death receptor, FAS; Fas ligand, FASL; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, TRAIL; matrix metalloproteinase, MMP; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, HIF-1α; vascular endothelial growth factor A, VEGFA; tumor protein P53, p53; growth arrest and DNA damage inducible alpha, GADD45α; cyclin-dependent kinase-1, CDC2; cell division cycle 25C, CDC25C; cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B, p27; caspase, cas; BH3 interacting-domain death agonist, Bid; B-cell lymphoma 2, Bcl-2; induced myeloid leukemia cell-differentiation protein Mcl, Mcl-1; B-cell lymphoma—extra large, Bcl-XL; BCL2-associated X, Bax; Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer, Bak; reactive oxygen species, ROS; mitochondrial ROS, mtROS; cytochrome C, Cyt C; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, MOMP; second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase, SMAC; X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, XIAP; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, PARP.