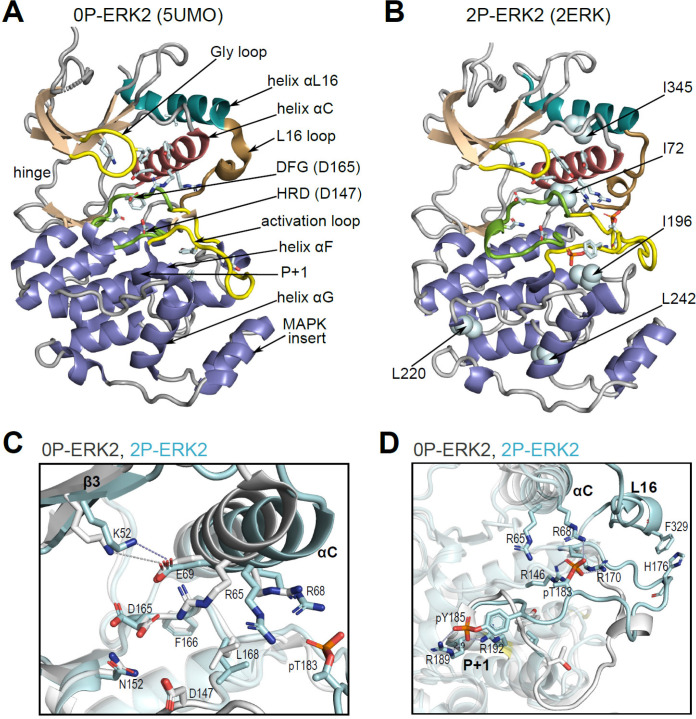
Figure 1. Structural features of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-2 (ERK2).
(A, B) X-ray structures of (A) 0P-ERK2 (PDBID:5UMO) and (B) 2P-ERK2 (PDBID:2ERK) apoenzymes. Panel A labels conserved motifs in ERK2 common to protein kinases. Panel B labels residues that illustrate L↔R exchange (I72, L220, L242; see Figure 2 and Figure 7), and key chemical shift perturbations (I196, I345; see Figure 8). (C) Structural superposition of 0P-ERK2 (white) and 2P-ERK2 (pale blue), illustrating overlapping positions of active site residues and an outward shift of helix αC upon dual phosphorylation. Root-mean-square deviations between 0P- and 2P-ERK2 for catalytic site residues were K52-0.69 Å, E69-0.16 Å, D147-0.055 Å, D165-0.88 Å. (D) Superposition of 0P-ERK2 and 2P-ERK2, illustrating conformational differences in the activation loop. In 2P-ERK2, pT183, and pY185 form ion pairs with multiple Arg residues, while the L16 loop folds into a 3/10 helix with side chain interactions to the activation loop. Structures were superpositioned by aligning Cα atoms within the C-terminal domain (residues 109–141, 205–245, 272–310).