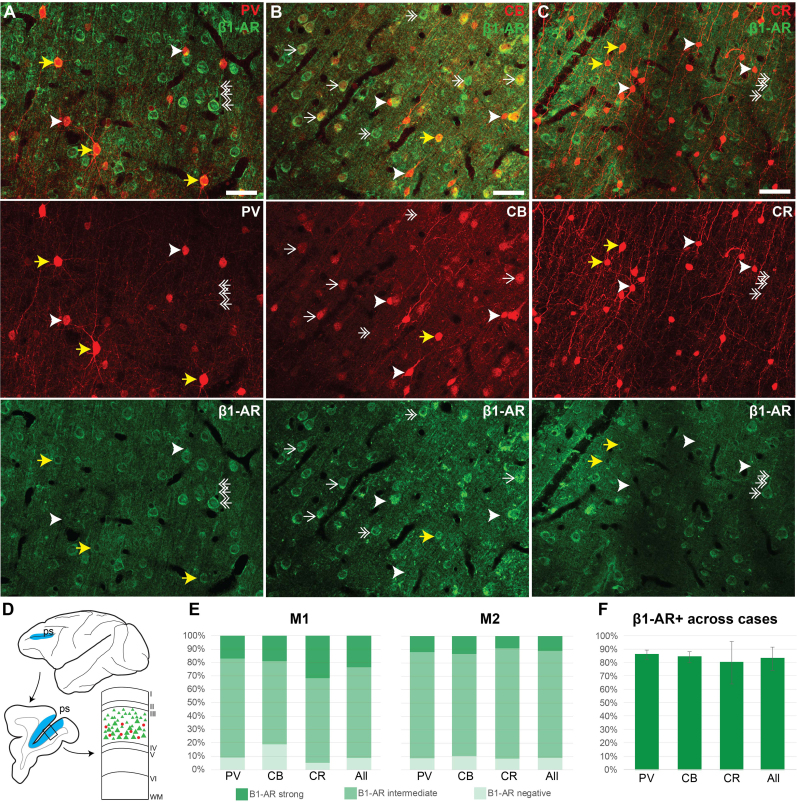
Fig. 1.
β1-AR expression across inhibitory neuron types in layer III dlPFC
Maximum projections of confocal microscopy photomicrographs depicting multiple label immunofluorescence (MLIF) in deep layer III dlPFC in a young macaque (8 years), depicting β1-AR with parvalbumin (PV) (A), calbindin (CB) (B), or calretinin (CR) (C). Yellow arrow, neuron double labeled for β1-AR (green), and PV, CB or CR (red). White arrowhead, neuron positive for PV, CB, or CR only. White double-headed arrow, pyramidal-like neuron positive for β1-AR and negative for PV, CB, or CR. White single-headed arrow, pyramidal-like neuron positive for β1-AR and lightly labeled by CB. (D) Schematic depicting exemplar sampling site (blue) in the mid to posterior principal sulcus (ps) of the dlPFC. Top, lateral surface of a macaque brain. Left, example coronal slice with sampling region along the principal sulcus (blue). Right, schematic of a cortical column depicting layer III, the region sampled for quantitative analysis. (E) Percent of PV, CB, or CR neurons that are β1-AR negative (light green, expression lower than sampled “neuropil” regions), β1-AR intermediate (intermediate green, expression above sampled “neuropil” regions, but less than expression observed in pyramidal-like neurons), or β1-AR strong (expression greater than β1-AR pyramidal-like neurons), sampled from two young monkeys (M1, 8 years, left; M2, 10 years, right). (F) Total β1-AR + neurons (β1-AR strong + β1-AR intermediate), averaged across M1 and M2, shown with standard deviation. In monkey 1 (M1), we analyzed 90 CB cells, 251 CR cells, and 250 PV cells. In monkey 2 (M2), we analyzed 136 CB cells, 211 CR cells, and 250 PV cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)