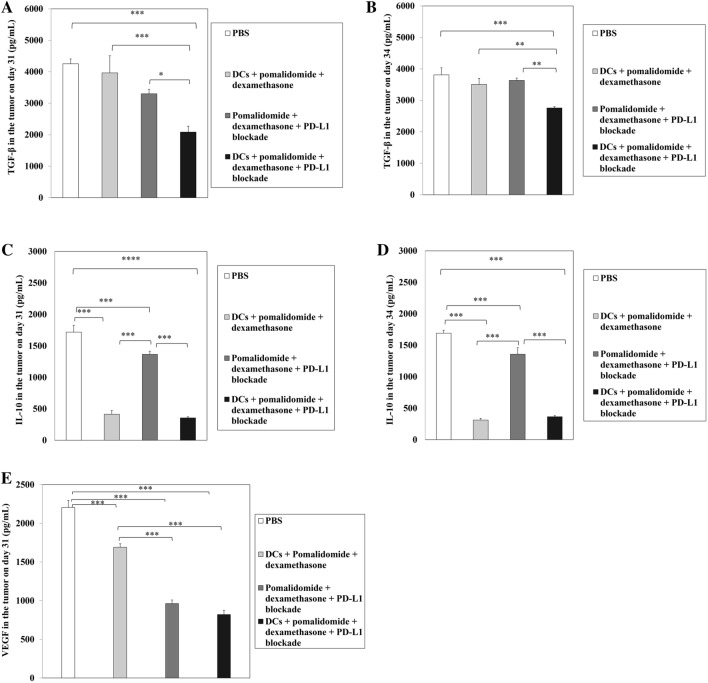
Fig. 7.
Reduced angiogenesis and inhibitory cytokine production by DC vaccination plus pomalidomide with dexamethasone and PD-L1 blockade in the tumor microenvironment of myeloma-bearing mice. Using flow ELISA, we measured the production of TGF-β, IL-10, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the tumor microenvironment of treated mice at days 31–34 after treatment. Compared to all treatment groups, the PBS control group had higher levels of TGF-β, IL-10, and VEGF production (***, P < 0.001). In contrast, the DC vaccination + pomalidomide with dexamethasone + PD-L1 blockade group exhibited significantly decreased production of TGF-β (a, b) compared to the other groups (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). Conversely, the groups treated with DCs had significantly decreased production of IL-10 (c, d) compared to the PBS control and pomalidomide with dexamethasone + PD-L1 blockade groups (***, P < 0.001). In comparison to the PBS control and DCs + pomalidomide with dexamethasone groups, treatment with pomalidomide/dexamethasone + PD-L1 blockade significantly decreased VEGF production (e) in the tumor microenvironment of treated mice (***, P < 0.001). These results suggested that combination therapy with DC vaccination + pomalidomide/dexamethasone + PD-L1 blockade suppressed angiogenesis and inhibitory cytokines by inhibiting TGF-β, IL-10 and VEGF production in the tumor microenvironment of myeloma-bearing mice. Data are representative of at least three experiments