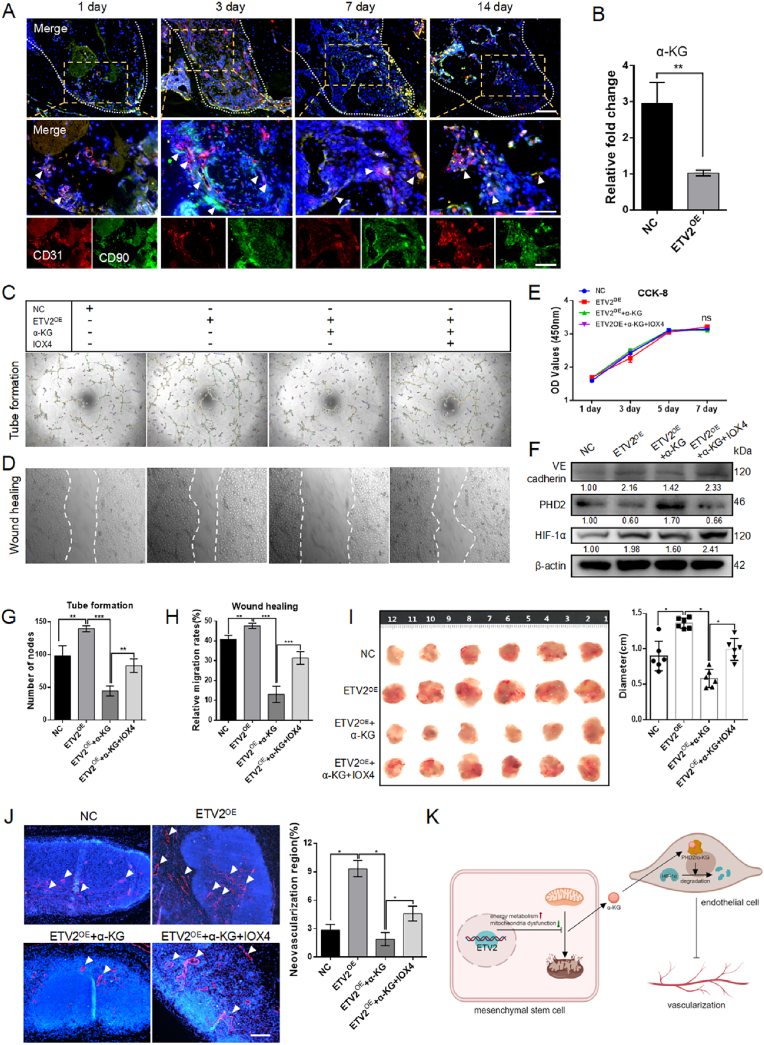
Fig. 5.
Reduction of α-KG promotes angiogenesis (A) Representative images of immunofluorescence co-staining CD31 (red) and CD90 (green) in a mouse tooth extraction model. The white arrows indicate the close proximity of CD31+ cells and CD90+ cells. Scale bar: 100 μm (B) α-KG content in the culture supernatant of an equal number of NC-DPSCs and ETV2-DPSCs (C) Tube formation of HUVECs treated with an ETV2-conditioned medium, with or without the incorporation of α-KG or IOX4 (D) The wound healing assay conducted on HUVECs treated with ETV2-conditioned medium, both with and without α-KG or IOX4 incorporation (E) The CCK-8 assay of HUVECs treated by ETV2 conditioned medium with or without α-KG or IOX4 (F) The protein expression of PHD2, HIF-1α, and VE cadherin in HUVECs treated by ETV2 conditioned medium with or without α-KG or IOX4 (G, H) The statistical analysis of node numbers and relative migration rates in C and D (I) Macroscopic images and size analysis of resected Matrigel plug (J) Representative images and neovascularization region statistics of immunofluorescence labeling CD31 in Matrigel plug. The areas exhibiting positive staining are denoted by the white arrows. Scale bar: 100 μm (K) Schematic illustration of mechanism of vascularization (NC, negative control; OE, overexpression. Data are presented as the mean of >3 independent experiments ±SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001).