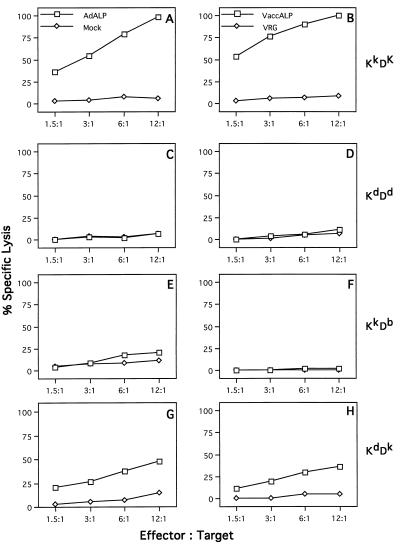
FIG. 8.
Identification of the MHC restricting element for ALP-derived epitopes in adenovirus-infected C3H mice. Splenocytes from three C3H mice infected with E1-deleted adenovirus expressing the ALP protein were isolated on day 7 after virus infection and restimulated in vitro for 5 days with ALP adenovirus. These effector cells were tested on target cells that differentiate H-2Kk and H-2Dk haplotypes. The MHC congenic target cell lines used were L929 cells (H-2KkDk) (A and B), KD2SV cells (H-2KdDd) (C and D), K2RSV cells (H-2KkDb) (E and F), and LC3H.OHSV (H-2KdDk) (G and H). Specific lysis was determined on target cells infected with adenovirus expressing the ALP protein (AdALP) (left panels) or recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the ALP protein (VaccALP) (right panels). Mock-infected cells were used as a negative control for adenovirus-infected target cells, whereas target cells infected with the recombinant vaccinia virus VRG expressing the rabies virus glycoprotein were used as a negative control for target cells infected with recombinant vaccinia virus. These data are from one of three experiments done; the standard deviations ranged from 8 to 12%, depending on the target cells. Spontaneous release was less than 10% for L929 and KD2SV cells, whereas it was 15 to 20% for K2RSV and LC3H.OHSV cells.