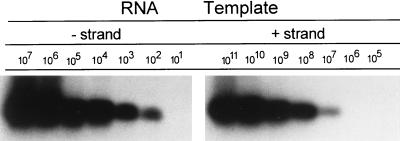
FIG. 1.
Sensitivity and specificity of RT-PCR using the Tth assay. Synthetic positive and negative strands were generated by in vitro runoff transcription with T7 RNA polymerase from a vector (pGEM-3Z) containing the 5′ untranslated sequence of HCV and serially diluted in water. The number of target template copies was calculated from optical density readings. A positive-sense primer was present during cDNA synthesis, after which the enzyme was inactivated by chelation with Mn2+ and then negative-sense primer was added. Samples were amplified as described in the text. Twenty microliters (20%) of the reaction mixture was fractionated on agarose, transferred to a nylon membrane by Southern blotting, and subsequently hybridized to a 32P-labeled probe. When 1 or 6 μg of total cellular RNA extracted from normal human liver tissue was added, the sensitivity of the reactions was lowered by no more than 1 log, while the specificity of the assay was not affected.