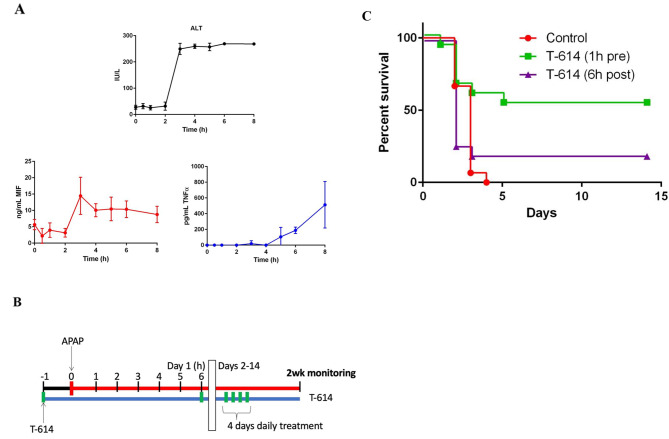
Fig. 3.
Early administration of T-614 prevents lethality in APAP overdose. (A) Serum concentrations of MIF peak with ALT, and prior to TNFα. C57BL/6 mice (n = 3–4/group) were given 300 mg/kg APAP intraperitoneally and euthanized at indicated time points for blood collection by cardiac puncture. Results are shown mean ± SD. (B-C) C57BL/6 wild-type mice (n = 10/group) were given 420 mg/kg APAP intraperitoneally in addition to T-614 vehicle (control) or T-614 initiated as pretreatment (1 h pre) or post-treatment only (6 h post) as described in Materials and Methods, and were monitored for two weeks; methods and time course are summarized in (B), and results are shown in (C). Death was not an endpoint for this experiment. A log-rank test was used to determine statistical significance: Control vs. T-614 (1 h pre), **p < 0.01; Control vs. T-614 (6 h post), p > 0.05. T-614 = iguratimod