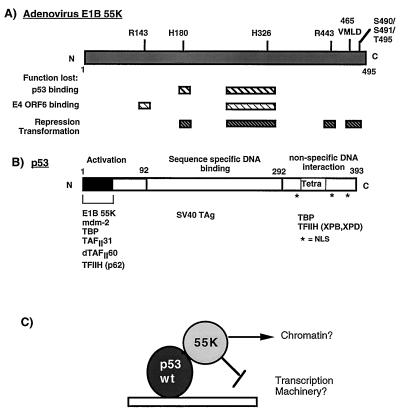
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram illustrating the functional domains in Ad E1B 55K (A) and the tumor suppressor p53 (B). (A) Hatched boxes indicate regions in E1B 55K which when mutated result in loss of the described functions. Positions where amino acids have been mutated by linker insertion or site-directed mutagenesis (57, 67) are indicated above the E1B 55K molecule. (B) The activation, DNA binding, and nonspecific DNA binding domains of p53 are indicated. The tetramerization domain (Tetra) is located in the C terminus. Nuclear localization signals (NSL) are indicated by asterisks. Proteins which are known to interact with the defined regions are indicated at the bottom. (C) Model of how E1B 55K may affect the activity of p53. E1B 55K may mediate alterations in chromatin structure or may target the general transcriptional machinery. SV40 TAg, simian virus 40 T antigen.