Figure 3.
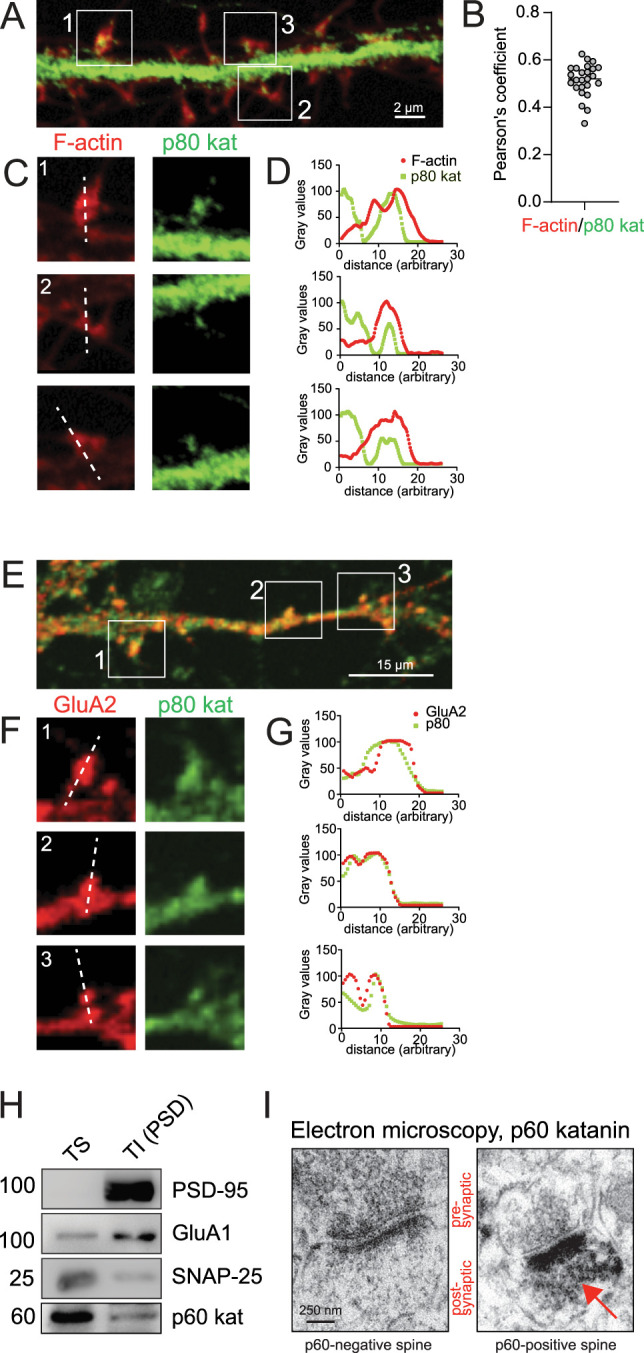
p60 and p80 katanin are located at excitatory spine synapses. A, Immunostaining of endogenous katanin p80 (green) and Rhodamine phalloidin labeling of F-actin (red), DIV13 neurons, three independent experiments. B, Pearson's correlation coefficient indicating colocalization of p80 katanin and F-actin. Mean ± S.E.M = 0.5149 ± 0.01379, n = 25 ROIs. C, Magnifications of spines from boxed regions in A. D, Fluorescence intensity profiles of line scans in C. E, Co-immunostaining of endogenous p80 katanin (green) and AMPAR subunit GluA2 (red), DIV13–16 neurons, three independent experiments. F, Magnification of boxed regions in E. G, Fluorescence intensity profiles of line scans in F. H, Western blot analysis of p60 katanin in Triton-X-100-soluble (TS) and Triton-X-100-insoluble (TI) synaptosomal fraction. The TI fraction is also known as PSD fraction, which is enriched for postsynaptic markers (PSD-95, GluA1), but contains very little presynaptic marker (SNAP-25). n = 3 experiments. I, Anti-p60 katanin immunoelectron microscopy with diaminobenzidine (DAB) showing a katanin-negative (left) next to a katanin-positive (right, red arrow) spine synapse from hippocampal neurons.
