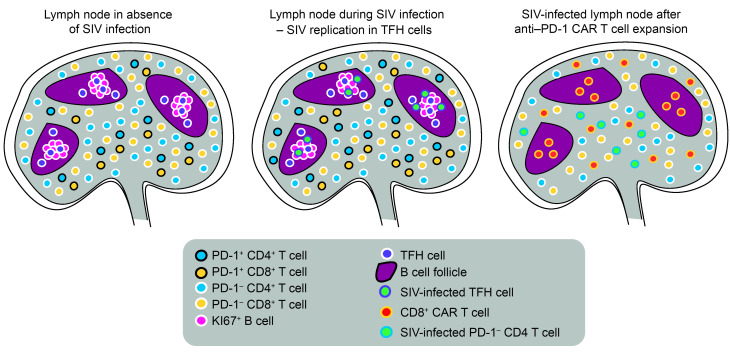
Figure 6. Effects of anti–PD-1 CAR T cells in SIV-infected RMs.
At steady state, TFH cells are localized in B cell follicles, where they support B cell responses. Extrafollicular PD-1–expressing T cells are part of the memory compartment or have been recently exposed to antigen. During lentiviral infection, there is an increase of TFH cells, extrafollicular PD-1+ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and viral replication occurring predominantly in TFH cells. During successful expansion, anti–PD-1 CAR T cells enter lymphoid tissues and kill extrafollicular PD-1+ T cells as well as TFH cells in the follicles. This results in relatively lower viral replication in the follicles due to depletion of TFH cells and increases viral replication in the extrafollicular T cell zone where it occurs in PD-1 CD4+ T cells. SIV-specific T cells are likely part of the extrafollicular PD-1+ T cell population and are lost due to depletion of anti–PD-1 CAR T cells. Over time, this leads to anti–PD-1 CAR T cell–mediated immunodeficiency.