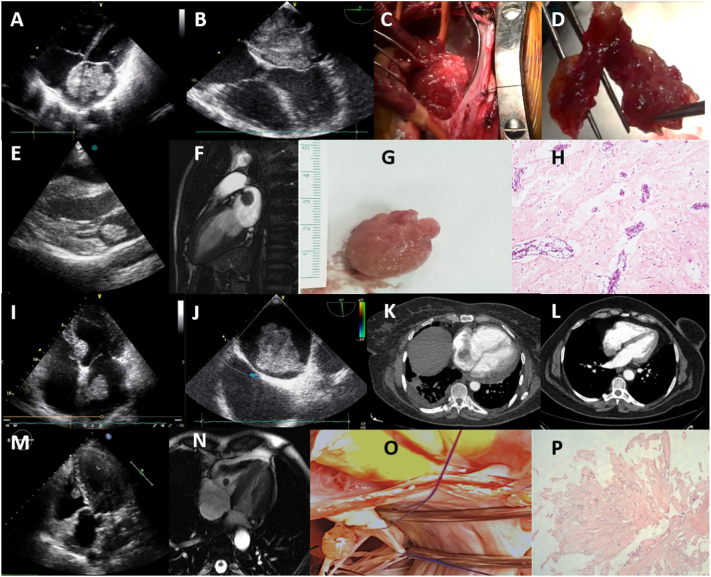
Fig. 1.
Primary benign tumors of the heart. (A) 2D TTE giant left atrial myxoma; (B) 2D TEE polylobulated myxoma, attached with a pedicle to the fossa ovalis (C) intraoperative view; (D) gross examination of the tumor, a dark red, fragile, polylobulated mass; (E) 2D TTE left atrial mobile, well circumscribed, ball shaped myxoma; (F) CMR SSFP cine, a hypointense mass with a short pedicle originating from the superior wall of the left atrium; (G) gross view of the surgically resected mass, smooth surface, bright pink colour (H) histology shows intense perivascular benign neoplastic cells and rare same type cells in myxoid stroma, compatible with myxoma, hematoxylin-eosin × 100; (I) 2D TTE pediculated left atrial myxoma originating from the interatrial septum; (J) 2D TEE, pediculated left atrial myxoma adjacent to the superior vena cava and patent foramen ovale; (K) CT, right atrial lobulated myxoma originating from fossa ovalis; (L) CT, myxoma originating from the posterior right atrial wall; (M) 2D TTE, a well-defined, nodular, mobile papillary fibroelastoma, originating from the anterior tricuspid leaflet chorda in the right ventricle; (N) CMR SSFP cine of the papillary fibroelastoma; (O) gross examination of the surgically resected papillary fibroelastoma, a translucent and gelatinous mass; (P) histology shows a benign tumor with multiple papillary fronds of different size that consisted of an acellular matrix and surrounded by single layer of endothelial cells, hematoxylin-eosin × 100.
2D TTE: two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography; 2D TEE: two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography; CMR: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; CT: computed tomography; SSFP: steady state free processing.