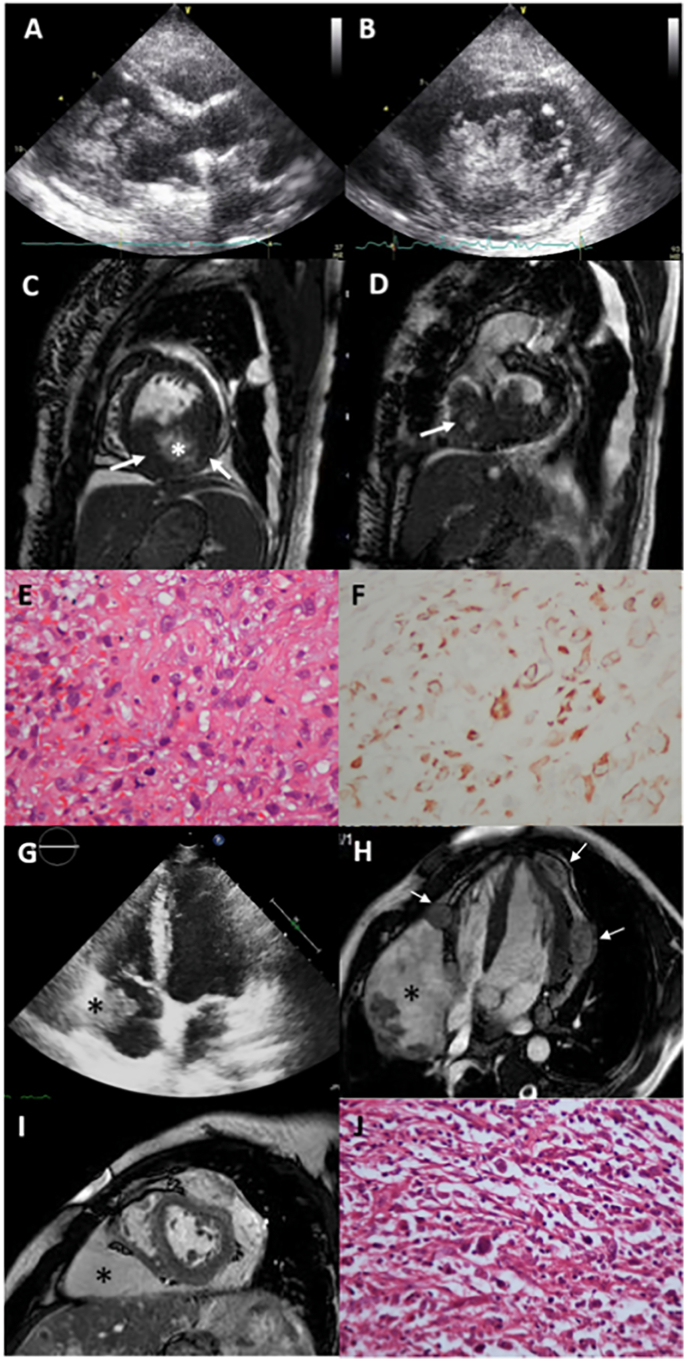
Fig. 2.
Primary malignant tumors of the heart.
Left ventricular endocavitary rhabdomyosarcoma; (A) 2D TTE, a polylobulated, mobile tumor filling the left ventricle; (B) 2D TTE short-axis view, tumor mass and extensions; (C) CMR, tumor originating from the inferior wall of the left ventricle (arrow) with cystic and necrotic areas at the centrum (*); (D) tumor also infiltrates the right ventricle (arrow); (E) histology: pleomorphic malign tumor cells of rhabdomyosarcoma, mitotic figures and atypical cells, hematoxylin-eosin × 200; (F) positive desmin immunochemistry in tumoral cells × 200.
High grade angiosarcoma; (G) 2D TTE tumor mass (*) in the right atrial cavity, infiltrating right atrial wall, (H) contrast-enhanced SSFP cine CMR, nodular lesions of the tumor (arrows) infiltrating left and right ventricular myocardium and epicardium, with a large mass of tumor in the atrioventricular groove and right ventricular myocardium (*) narrowing the right heart chambers; (I) CMR, short axis SSFP, large tumor mass (*); (J) High grade angiosarcoma, irregular malignant spindle cells haphazardly arranged, hematoxylin-eosin × 40.
2D TTE: two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography; CMR: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, SSFP: steady state free processing.