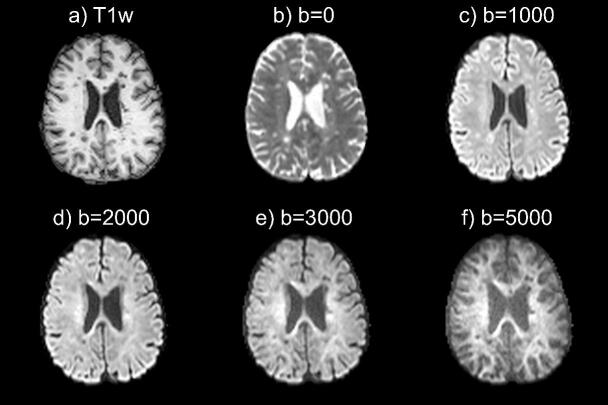
Fig. 2.
Axial T1- (a) and average diffusion-weighted MRI (b-f) images of a 28-year-old woman with RRMS showing the influence of b-value in the sensitivity for specific brain tissue. Higher b-values (b=3000, b=5000 s/mm2) are more sensitive to white matter and white matter alteration (i.e. lesions), but noisier compared to lower b-values (b=1000 s/mm2).