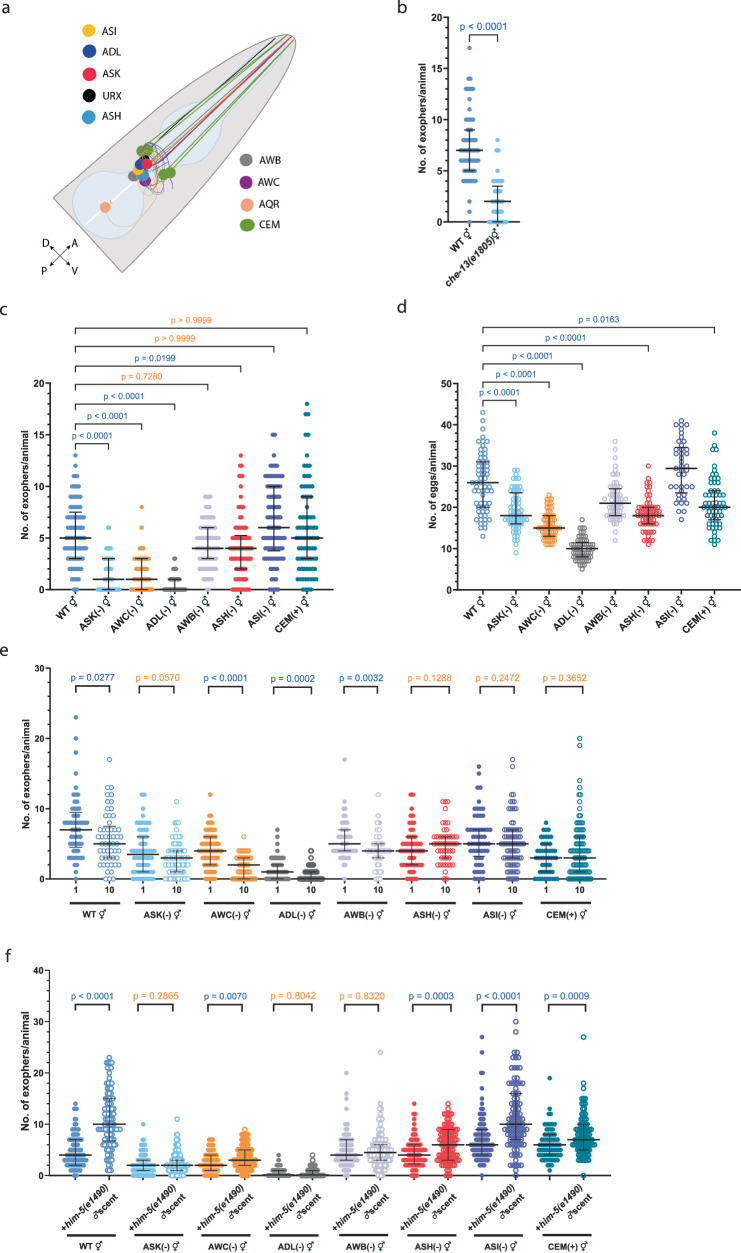
Fig. 4. Multiple olfactory neurons regulate exophergenesis levels in response to hermaphrodite and male pheromones.
a Sensory neurons investigated within this study. b Hermaphrodites with impaired ciliated sensory neurons exhibit reduced exophergenesis. n = 66 and 65 worms (for respective columns), N = 3 independent experiments. c Genetic ablation of ASK, AWC, ADL, or ASH neurons reduces exopher production in hermaphrodites grown in higher-density populations. n = 97, 61, 62, 90, 83, 90, 90, and 79 worms (for respective columns), N = 3 independent experiments. d Worms with genetically ablated neurons, resulting in reduced exophergenesis, also exhibited fewer eggs in utero. n = 61, 61, 61, 61, 61, 61, 41, and 61 worms (for respective columns), N = 2 - 3 independent experiments. e Decreased exophergenesis level due to exposure to hermaphrodite pheromones is mediated by ASH, ASI, and ASK neurons and can be altered by adding CEM male-specific neurons. A schematic representation of the experimental setup is presented in Fig. 2a. n = 57, 53, 62, 82, 84, 53, 88, 96, 49, 66, 55, 50, 56, 86, 50, and 88 worms (for respective columns), N = 3 independent experiments. f Increase in exophergenesis levels due to exposure to male pheromones is mediated by ASK, AWB, and ADL neurons. A schematic representation of the experimental setup is presented in Fig. 1e (without conditioning with WT males). n = 106, 98, 99, 108, 101, 100, 98,106, 94, 98, 92, 95, 101, 90, 77, and 89 worms (for respective columns), N = 3 independent experiments. Data information: Data are presented as median with interquartile range; not significant p values (p > 0.05) are in orange color, significant p values (p < 0.05) are in blue color; (b, e, f) two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, (c, d) Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.