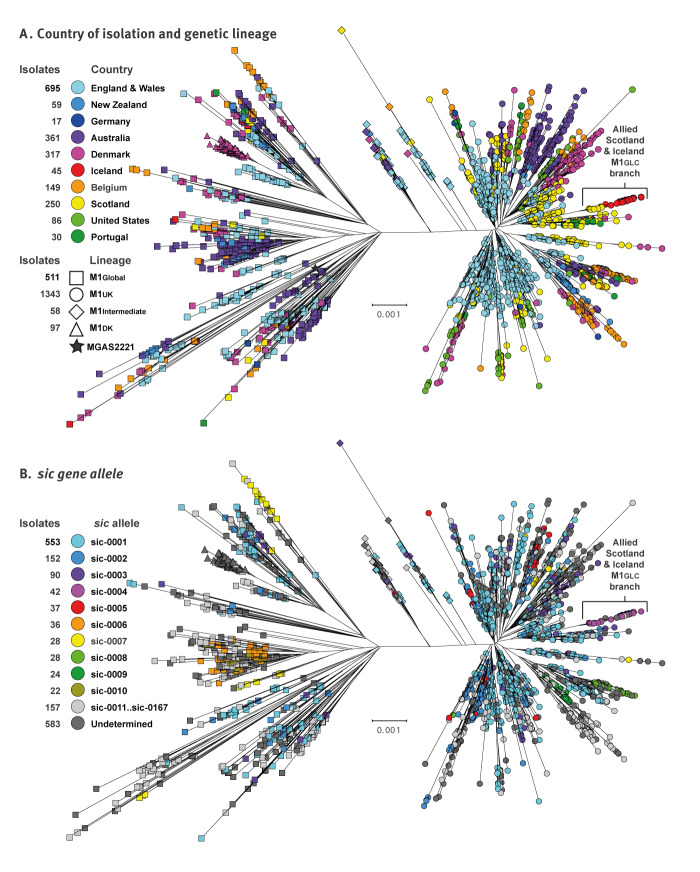
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationships among contemporary group A streptococcus M1 isolates, 2005–2023 (n = 2,009)
Phylogeny for 2,009 GAS M1 isolates by inferred neighbour-joining based on 8,599 core chromosomal SNPs identified by Illumina short-read whole genome sequencing read mapping relative to reference strain MGAS2221 (NCBI accession number CP043530). Panel A: isolates are coloured by country of isolation and shaped by M1 genetic lineage. Panel B: isolates are coloured by the 10 most prevalent sic gene alleles in descending order.
With current short read sequencing technology it is problematic to assemble reads containing multiple different repeat domains, such as the sic gene, and accurately map them to a reference strain containing such repeat structures. The variants labeled ‘undetermined’ are isolates in which a consensus assembly of the sic gene was not obtained using the Illumina short-read-length sequencing data. This is likely because the sic gene in these isolates had more repeats or a more complex set of repeats that confounded the SPAdes assembler.