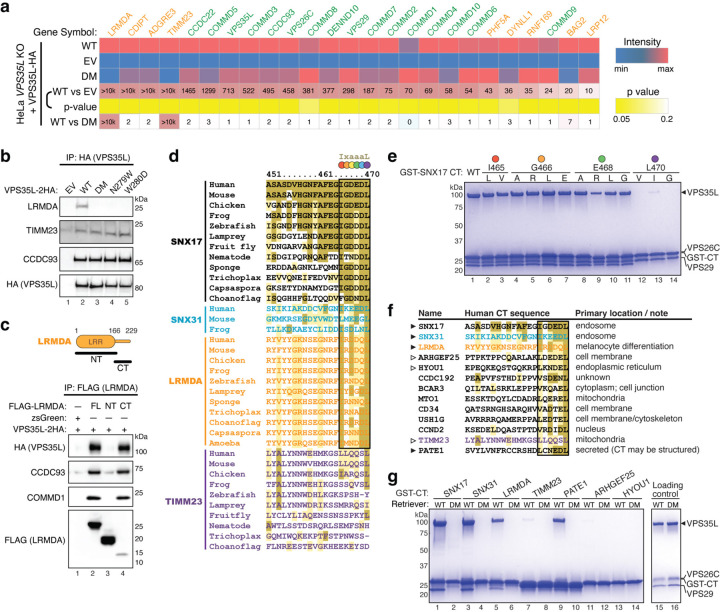
Fig. 5. Interactome analysis reveals other Retriever ligands with an acidic CT tail.
a. Heat map of VPS35L-interacting proteins quantified by mass spectrometry after coimmunoprecipitation of HA-tagged VPS35L, using indicated HeLa stable cell lines shown in Fig. 3d. Protein spectral counts, fold change between indicated cells, and corresponding p-values are depicted. Components of CCC and Retriever are highlighted in green, while other proteins are marked in orange. b. Immunoprecipitation of VPS35L (HA) followed by immunoblotting for LRMDA, TIMM23, and CCDC93 in indicated stable HeLa cell lines. c. Immunoprecipitation of LRMDA full-length (FL), NT, and CT in Lenti-X 293T cells, followed by immunoblotting for indicated Retriever and CCC subunits. d. Sequence alignment of the CT tail of indicated proteins across representative species. Gold, light-gold, and white shading denote sequences identical to, similar to, and not conserved with the human SNX17 CT sequence, respectively. The identified 6-residue acidic sequences are highlighted by the black box, with each position denoted by a colored dot corresponding to the residues mutated in (e). e. Coomassie blue-stained SDS PAGE gel showing in vitro pull-down of Retriever by GST-SNX17 CT tails containing indicated point mutations. f. Sequence alignment of the CT tail of indicated proteins in humans, of which the last six residues concur to the motif [LVI]-X-[DEQN]-X-[DEQN]-L and exist in unstructured tails. Gold, light-gold, and white shading denote sequences identical to, similar to, and not conserved with the human SNX17 CT sequence, respectively. g. Coomassie blue-stained SDS PAGE gel showing in vitro pull-down of Retriever WT vs. the DM mutant by GST-tagged CT acidic tails of the indicated proteins.