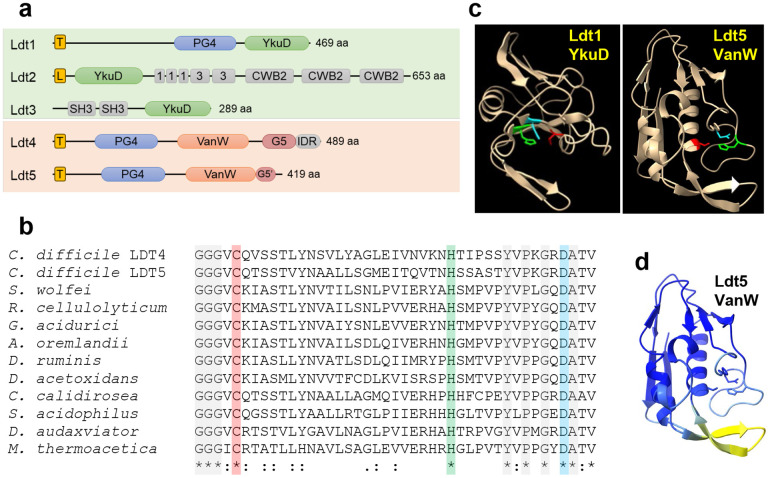
Fig. 2. Predicted structures of C. difficile Ldts.
(a) Domain architecture. T, transmembrane helix; L, signal peptidase 2 signal sequence; PG4, PG binding domain 4; YkuD, L,D-transpeptidase catalytic domain; 1 and 3, choline binding domains; CWB2, cell wall binding domain 2; SH3, Bacterial SH3 domain; VanW, L,D-transpeptidase catalytic domain; G5 and G5’, complete and partial G5 domains; IDR, intrinsically disordered region. (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of the active site region from 10 VanW domains with the proposed catalytic triad highlighted with red, green and blue. Gray highlight and asterisks denote strict amino acid identity, colons and periods indicate other conserved positions. Sequences shown are from C. diffficile, Desulforudis audaxviator, Moorella thermoacetica, Sulfobacillus acidophilus, Ruminiclostridium cellulolyticum, Gottschalkia acidurici, Alkaliphilus oremlandii, Syntrophomonas wolfei, Desulforamulus ruminis, Desulfofarcimen acetoxidans, and Chthonomonas calidirosea. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for an alignment of the entire VanW domains. (c) Alphafold2 models of the YkuD domain from C. difficile Ldt1 and the VanW domain from Ldt5, with the catalytic triads in color: Cys (red), His (green), Asp (cyan). (d) Confidence of the Ldt5 VanW domain model based on predicted local distance difference test. Dark blue >90 (highly accurate), light blue 89-70 (modeled well), yellow 69-50 (low confidence, caution).