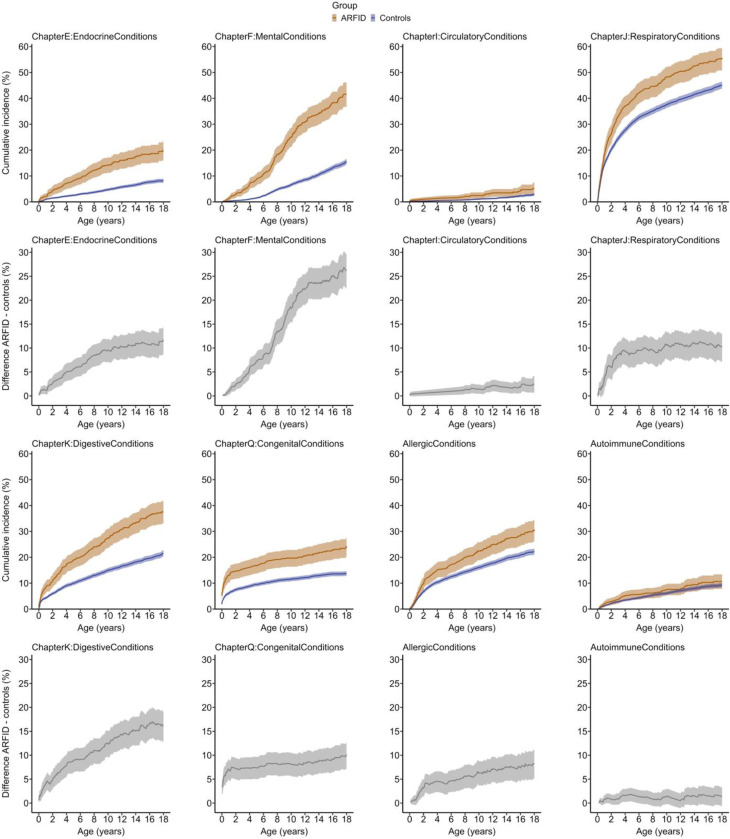
Figure 4. Cumulative incidence plots for co-existing conditions in children and adolescents with ARFID vs. controls.
Absolute risk via cumulative incidence (%) of having a specific condition (ICD-chapters and grouped allergic and autoimmune conditions) and lower and upper limits of its cluster-robust 95% confidence interval are plotted over age (0 to <18 years) in ARFID vs. controls. As a follow-up analysis, difference (%) in cumulative incidence was computed as ARFID - controls and plotted for each condition below the corresponding cumulative incidence plot. Perinatal conditions were excluded given their occurrence during the perinatal period and lack of age-related dynamics. Cumulative incidence was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method (1 - Kaplan-Meier survival estimate, accounting for censoring) after creating a modified analysis sample by matching n=10 unexposed individuals to each (n=1) individual with ARFID, stratified by sex and birth year. Abbreviation: ARFID, avoidant restrictive food intake disorder.