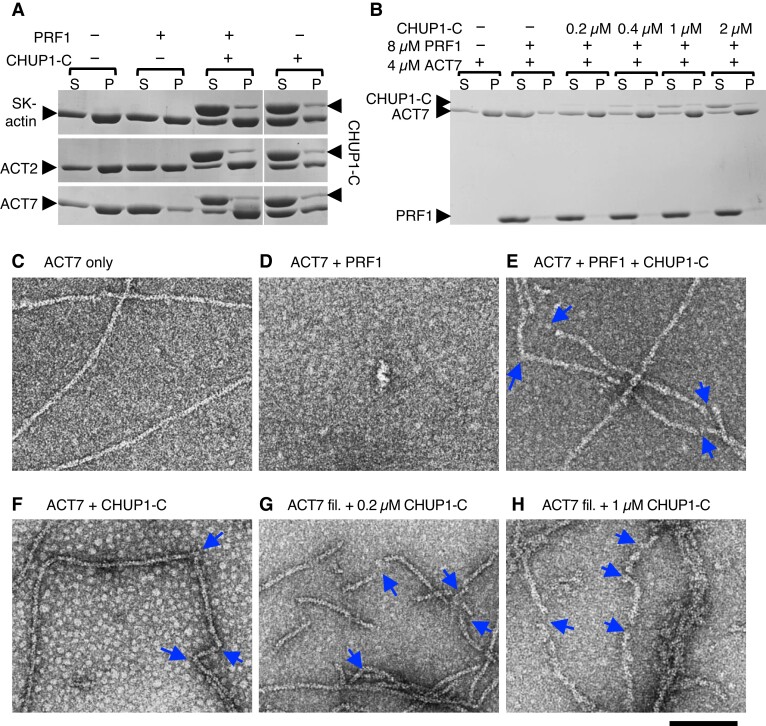
Figure 5.
Interaction of CHUP1-C with actin filaments in vitro. A) Ultracentrifugation assays of the effects of profilin and CHUP1-C on actin polymerization. Rabbit skeletal muscle actin (SK-actin) or Arabidopsis ACT2 or ACT7 was allowed to polymerize in F-buffer 1 in the presence or absence of 8 μM PRF1 and 4 μM CHUP1-C. After ultracentrifugation, the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were separately run on SDS-PAGE. B) Similar to A), except that only ACT7 was used and the concentration of CHUP1-C varied from 0 to 2 μM. C to F) Electron micrographs of actin polymerized in the presence or absence of profilin and CHUP1-C for 20 min. In C to F), 4 μM ACT7 was allowed to polymerize in F-buffer 1 in the absence of PRF1 and CHUP1-C C), in the presence of 4 μM PRF1 D), in the presence of 4 μM PRF1 and 0.4 μM CHUP1-C E), and in the presence of 0.4 μM CHUP1-C F). Actin solutions were diluted to 0.7 µM ACT7 in EM buffer, and then fixed and negatively stained with uranyl acetate. For particles observed in F), see Supplementary Fig. S7C. G and H) ACT7 filaments polymerized in the absence of PRF1 and CHUP1-C were diluted to 0.7 µM and applied onto an EM grid. After ∼30 s, 0.2 µM G) or 1 µM H) CHUP1-C was added, and the sample was negatively stained within several seconds. Blue arrows indicate the positions of sharp bent or gap of actin filaments. Scale bar, 100 nm.