Extended Data Fig. 4. AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq enriches a complex set of clonotypes from PBMC after mRNA vaccination of previously SARS-CoV-2 infected persons.
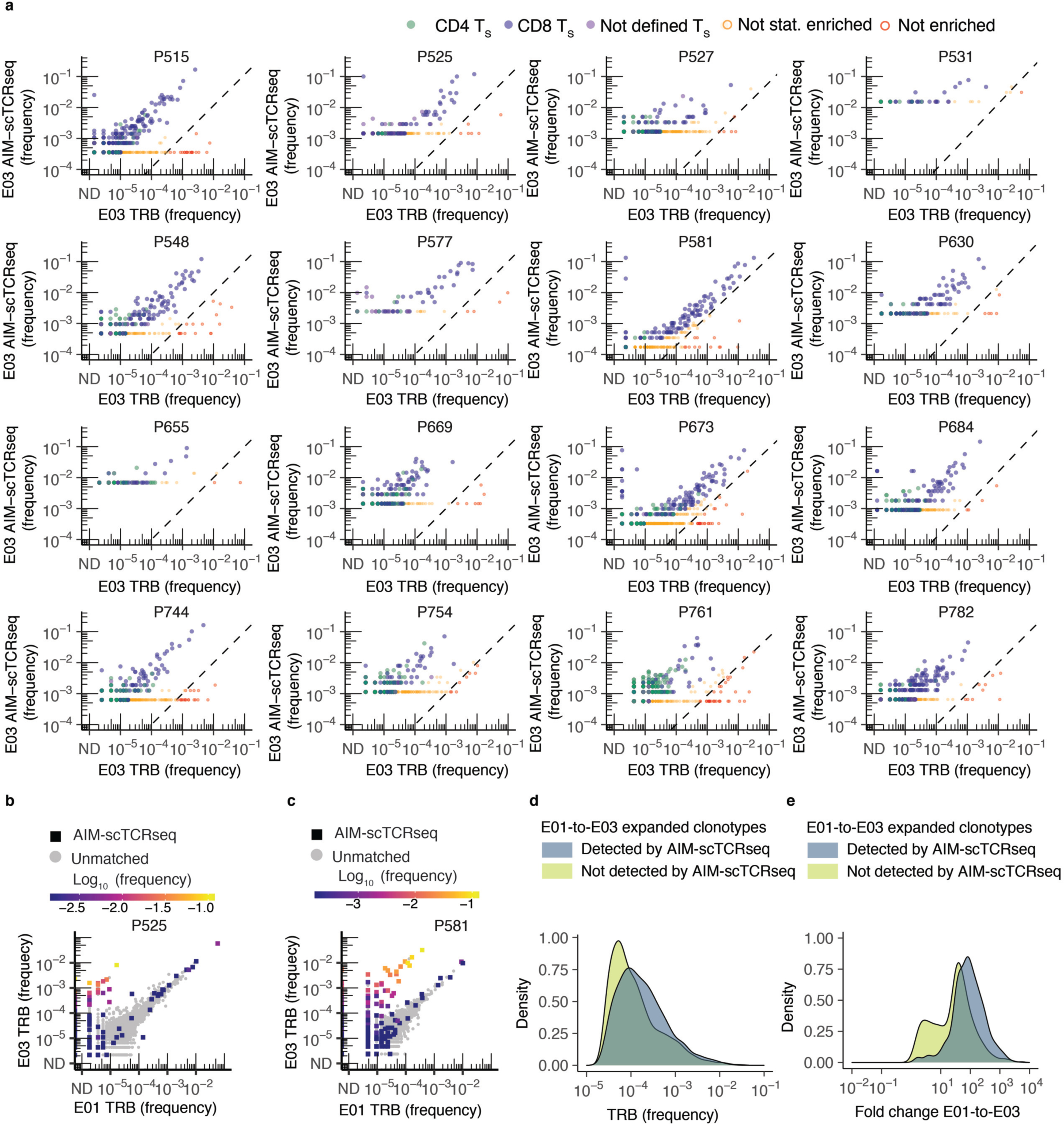
(a) Frequency of clonotypes detected by CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq plotted against the productive frequency of TRB-matched templates in bulk TRB sequencing at E03. Cell types defined by oligonucleotide-labeled mAbs are shown as CD4+ (green), CD8+ (blue), or phenotype not defined (purple) T cells. Clonotype enrichment in CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq was determined by cumulative distribution function (CDF) with false discovery rate (FDR) correction (Methods). Clonotypes that were detected, but not enriched, in CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq are shown in red (n = 180) and were omitted from CDR3 motif discovery analysis. UND indicates clonotypes that could not be assigned a TCRB unambiguously. (b,c) Productive frequency of CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq detected clonotypes in relation to change in productive frequency from E01 to E03 in bulk TCR-β-seq is shown for 2 representative participants, including one with a lower proportion of representation in CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq of their significantly expanded clonotypes (P525, b) and another with a higher proportion of significantly expanded clonotypes also seen by CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq (P581, c). (d,e) Density plots show proportion of unique, expanded clonotypes by frequency at E03 (d) or fold change from E01 to E03 (primary vaccination) (e) by detection in CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq at E03 amongst 12 participants with both paired E01/E03 bulk TCR-β-seq and CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq.
