Extended Data Fig. 8. Selection of AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq T cells using CD69, CD137, and CD134/ CD154 marker sets compared to bulk TCRβ-seq and sorted CD4 TCRβ-seq from PBMCs from E01 to E03.
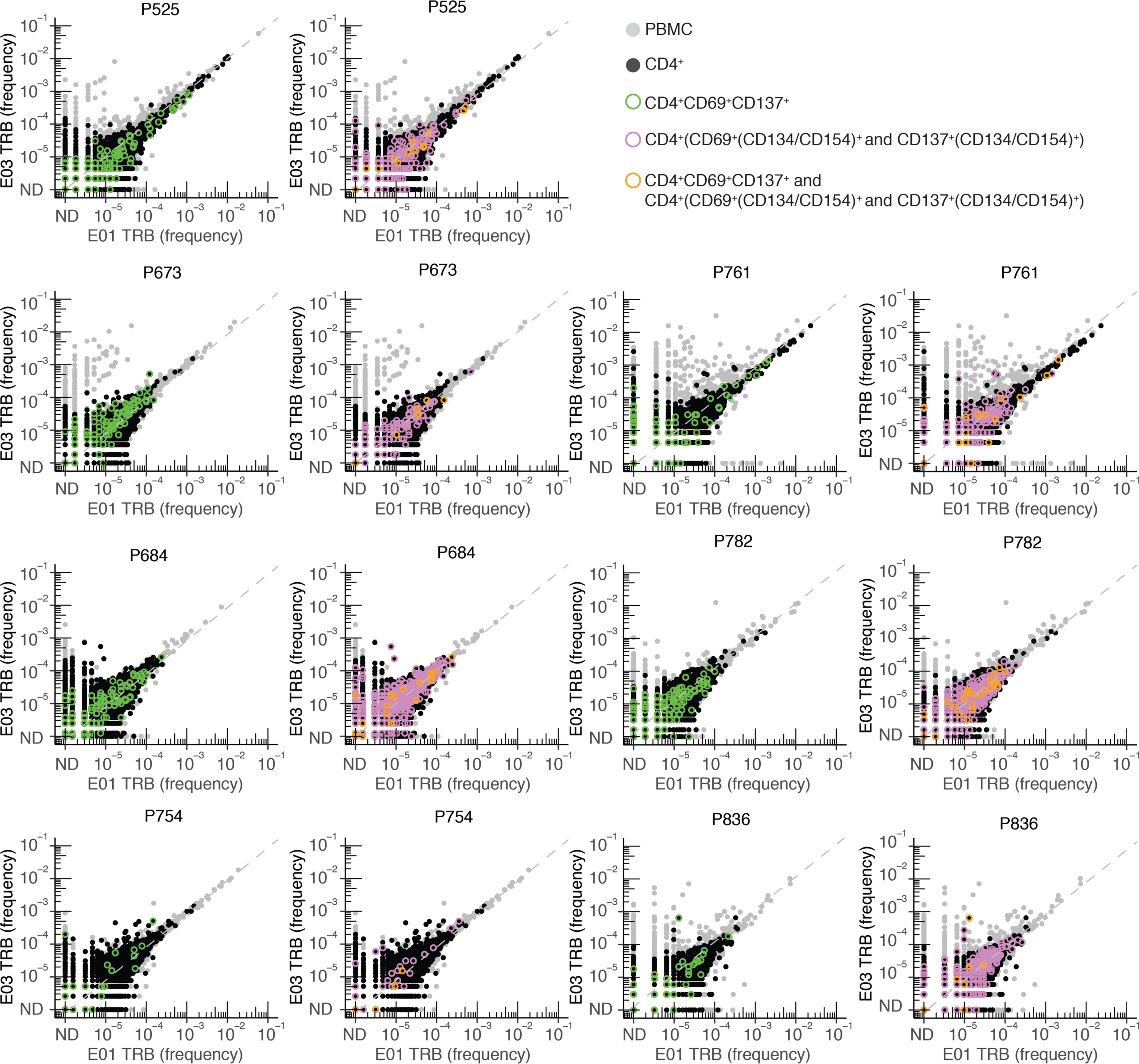
Frequency (% of bulk TRB repertoire) of individual clonotypes in E01 vs. E03 in 7 persons studied by CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq and (CD69/CD137)+(CD134/CD154)+ CD4+ AIM-TCRβ-seq. Dotted line indicates y = x. Participant ID at top of each pair of graphs. ND = not detected. All PBMC are shown. Clonotypes found in the total CD4+ sorted fraction are shown in black. Clonotypes present in the total CD4+ sorted fraction and also enriched in sequential sorting of CD4+CD69+CD137+ (green) cells are overlaid with CD4+CD69+(CD134/CD154)+ and CD4+CD137+(CD134/CD154)+ (pink) cells in the left and right panels, respectively, for seven participants. Clonotypes in all three fractions (total CD4+, CD4+CD69+CD137+, and CD4+CD69+(CD134/CD154)+ and CD4+CD137+(CD134/CD154)+) are shown in orange. Gray shaded clonotypes were not identified as CD4+ by any of these methods.
