Fig. 2. Longitudinal kinetics of S-reactive clonotypes defined by AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq from post-infection to post-vaccination.
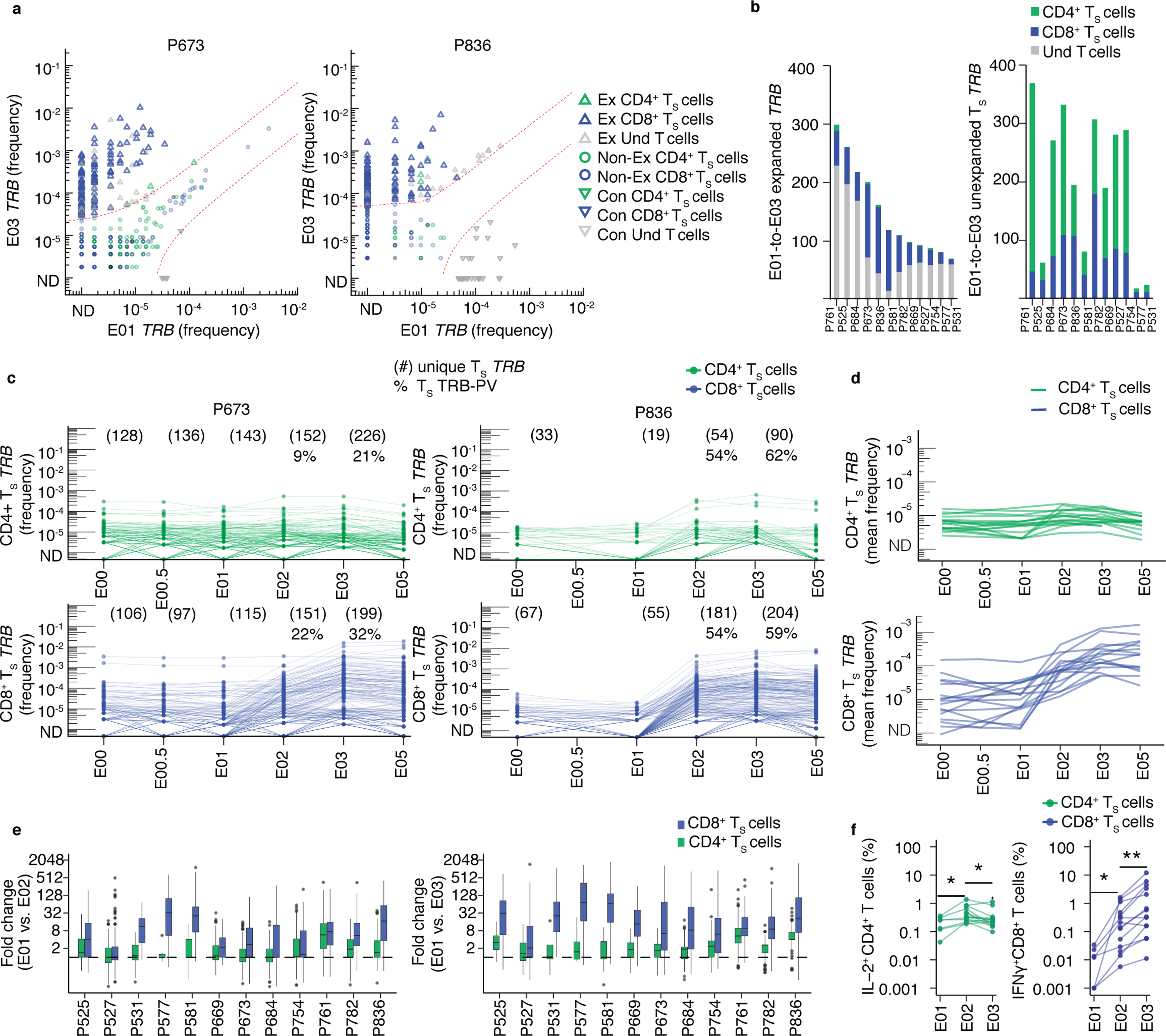
(a) Overlay of TRB sequences from CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq of TS cells onto bulk TRB clonotype frequency at E01 and E03 in two representative participants. E01-to-E03 expanded (Ex), non-expanded (non-Ex) or contracted (Con) TRB clonotypes for TRB sequences matching CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq (TS) and unmatched TRB sequences (undetected, Und) are shown. (b) Numbers of expanded or non-expanded PBMC TRB-defined clonotypes matching CD8+ or CD4+ TS clonotypes in 12 participants with E01-E03 expanded samples. (c) Longitudinal tracking of CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq-identified CD4+ and CD8+ TS TRB clonotype abundance in PBMC of two representative participants. The number of unique CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq TRB clonotypes from E03 detected at each time point are shown. Percentages represent CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq TRB-PV clonotypes for the E02 and E03 timepoints. (d) Mean abundances of S-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clonotypes identified by CD69+CD137+ AIM-scTCRɑβ-seq in 17 participants at E00 to E05. (e) Distribution of fold-changes (median, box (IQR), and whiskers (1.5 * IQR)) observed for S-reactive CD4+ or CD8+ T cell clonotypes between E01 and E02 and E01 and E03. (f) Intracellular cytokine staining after stimulation of PBMC isolated at E01 (n=7), E02 (n=14) and E03 (n=14) with S peptides. Level of statistical significance by paired, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test is indicated *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
