Fig. 2. Sequence conservation at the SRY locus.
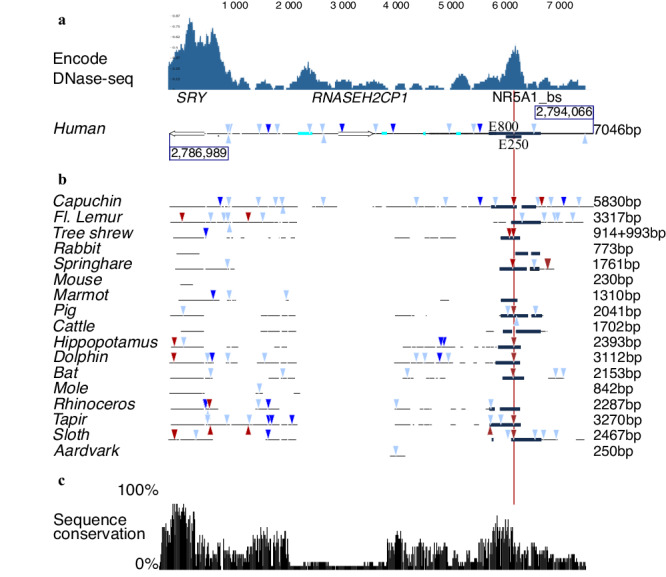
a The profile of accessible chromatin, determined by DNase-seq, was downloaded from the Encode project (https://www.encodeproject.org/, experiment ENCSR729DRB, embryonic human testis). It reveals two distinct regions of accessible chromatin, one encompassing the SRY gene and the other corresponding to the E250 region, centered on the predicted NR5A1 binding site (NR5A1_bs). The graphical representation of the human SRY locus is shown below, in phase with the DNase-seq profile, and the corresponding number of base pairs is indicated on the right. GATA4 (light blue), WT1 (dark blue), and NR5A1 (red) Matinspector predicted binding sites are indicated as in Fig. 1b. E800 corresponds to the region sequenced in 46,XY individuals with unexplained gonadal dysgenesis. E250 corresponds to the 250 bp fragment used in the luciferase assay (Fig. 4e). Repetitive sequences are shown in turquoise, the SRY gene, and RNASEH2CP1 pseudogene Open Reading Frame as open arrows. b DNA fragments from eutherian representative species, aligned to the 7046 bp human sequence shown in a. The sequences homologous to E800 are shown in black. The conservation of these sequences across a diverse range of species, including sloth, human, springhare, pig, bat, and tapir, indicates that this region was already present in their last common ancestor. Similarly, the presence of an NR5A1 predicted binding site in a homologous position shown by a red line in these species suggests a role for this NR5A1 binding site early in eutherian radiation. The total number of bases aligned to the human sequence for each species is indicated on the right. c The species presented in Fig. 2b were selected to represent diversity in the eutherian radiation. An estimate of sequence conservation is given. Where sequences could be aligned, a 100% conservation means that a nucleotide is conserved in all the 18 sequences. A conservation of 50% would mean that for a given aligned nucleotide, it is conserved in only half of the species. The SRY gene and E800 sequences both show the highest percentage of sequence conservation in the region.
