Fig. 4. In silico and in vitro analysis of E250 function.
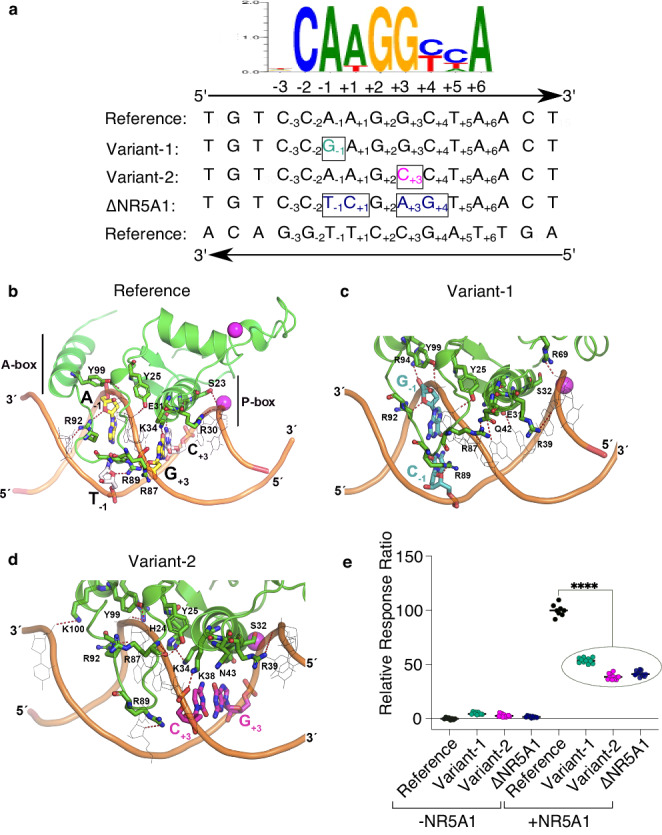
a Alignment of the sequence flanking the NR5A1-binding site (GRCh38-chrY: 2,792,790-2,792,804), in the reference genome (Reference), mutated in the familial case (Variant-1), in the sporadic case (Variant-2), and in a negative control with four substitutions disrupting the core sequence (∆NR5A1). The NR5A1 consensus binding site is shown above for comparison, featuring the core element from +1 to +6 and the flanking sequence from −1 to −3. b–d Schematic representation of NR5A1 DNA-binding domain (DBD) interactions with E250 variants based on the crystal structure of NR5A1 bound to the inhibin-A promoter. Protein residues of NR5A1 are depicted in green, while the DNA backbone is shown in orange. Hydrogen bond contacts are represented as red dashed lines. b Structural model of wild-type NR5A1 bound to DNA. The two paired binding site residues of interest are shown, based on the sequences in panel A (A-1/T- 1 and G + 3/C + 3). NR5A1 binds to DNA primarily as a monomer. The protein P-box region (codons 31 to 35) interacts directly with the core binding motif (+1 to +6), whereas the A-box protein region (codons 89 to 92) interacts with the flanking DNA sequence (−1 to −3). c, d Structural models of wild-type NR5A1 bound to variant response elements associated with testicular dysgenesis. In Variant-1 (panel c), the A > G purine to purine change at nucleotide −1 in the flanking sequence (shown in cyan, with corresponding reverse strand T > C change) affects interactions between the DNA and A-box residues changing the H-bond pattern between DNA and basic residues R87, R89, R92, R94, and Y99 of NR5A1. In contrast, with Variant-2 (panel d), the G > C purine to pyrimidine change at nucleotide +3 (shown in magenta, with corresponding reverse strand C > G change) affects interactions between the DNA and P-box. There is disruption of critical H-bond interactions that would typically occur between NR5A1 codon K38 and the DNA amine group of G9, and between codon E31 with the amine group of C22; furthermore, the amine group of codon K34 is neutralized by H24 and E31 in NR5A1. These changes induce a displacement of both “A-box” and “P-box” helices that may influence binding affinity or kinetics. e Transient gene transfection assay showing activation of a luciferase reporter construct containing the wild-type or variant E250 response element co-transfected with or without NR5A1 in HEK293T cells (12 technical replicates, outliers identified by the interquartile Range (IQR) method and then removed, with comparison performed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum exact test (p value = 1.379e-08****) in R.
