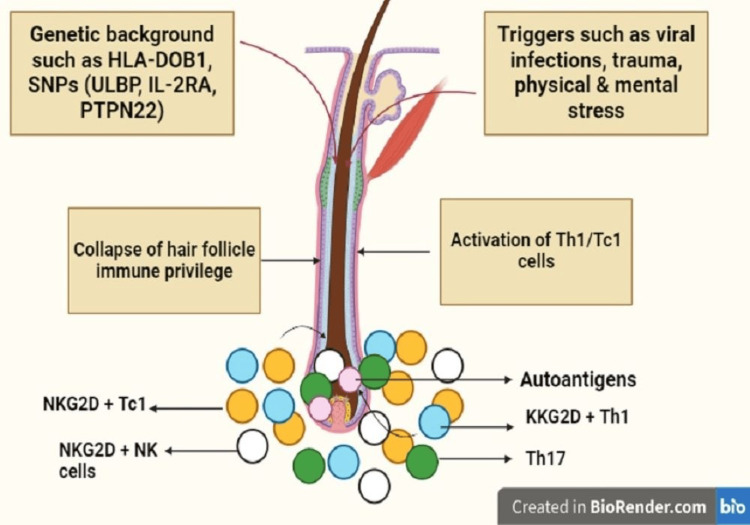
Figure 2. Pathogenesis of alopecia areata.
Within a genetic predisposition, various triggers, such as viral infections, trauma, and physical/emotional stresses activate autoreactive CD8+ T cells and Th1 cells, leading to the production of IFN-?. IFN-?, in turn, increases the expression of CXCL10 and stimulates the production of IL-15, along with its chaperone receptor IL-15Rα by hair follicle keratinocytes in the outer root sheath. Additionally, IFN-? disrupts the immune privilege of hair follicles, exposing autoantigens to autoreactive CD8+ T cells. Chemotactic activity towards CXCL10 is exhibited by Th1 and Tc1 cells, with the effector cell being NKG2D+CD8+ T cells in alopecia areata pathogenesis.