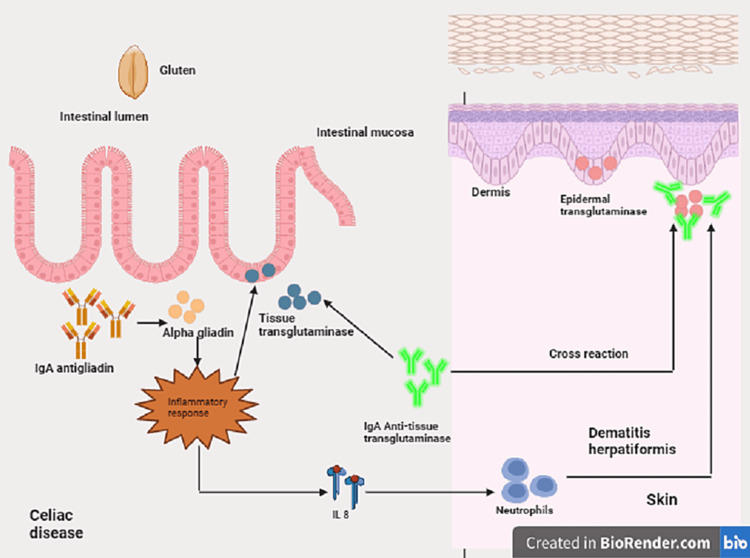
Figure 6. Pathogenesis of dermatitis herpetiformis.
The major environmental factor involved in triggering the disease is exposure to gluten. Gluten is composed of two peptides, gliadin and glutenin. The fraction linked to intestinal disease is from the gliadin, and its immunoreactivity is due to the N-terminal. In addition to antibodies directed precisely against gliadin in the intestinal mucosa, the formation of specific antibodies against autoantigens, such as transglutaminases, may also occur. Epidermal transglutaminase (ETG) is present in keratinocytes and maintains the stratum corneum's integrity. It performs its function by connecting the various epidermal structural proteins. Tissue transglutaminase (TTG) is the main antigen for CD antibodies, as ETG is the antigen in DH. Anti-TTG antibodies may, by cross-reaction, recognize ETG, leading to the onset of cutaneous IgA deposits.