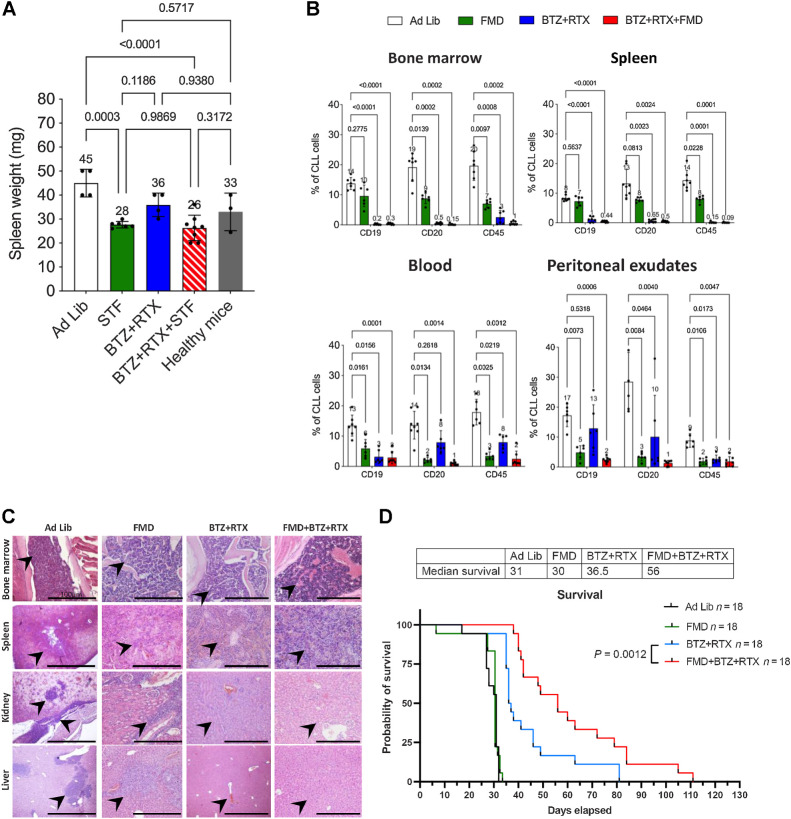
Figure 6.
Cyclic FMD plus bortezomib + rituximab retards CLL progression in an intravenous CLL model. A, Spleen weight (mg) modifications over the time and under the indicated treatment conditions are represented. B, Effect of FMD, bortezomib + rituximab, or their combination, on the percentage of CLL cells in the bone marrow, spleen, blood and peritoneal exudates, as evaluated by FACS analysis. At the end of experimental procedures, cells collected from the indicated organs or tissues were analyzed by flow cytometry after staining with mAb against human CD19, CD20, and CD45 to identify leukemic B cell populations. Ad lib + Vehicle, N = 8; FMD: Fasting-mimicking diet + vehicle, N = 6; bortezomib + rituximab: Ad lib + bortezomib (0.35 mg/kg) + rituximab (10 mg/kg) once a week for 3 weeks (days 7, 14, 21), N = 7; FMD + bortezomib + rituximab: FMD + bortezomib (0.35 mg/kg once a week) + rituximab (10 mg/kg) once a week for 3 weeks (days 7, 14, 21), N = 7. C, H&E staining of bone marrow, spleen, kidney, and liver. Ad lib + Vehicle, N = 8; FMD: + vehicle, N = 6; bortezomib + rituximab: Ad lib + bortezomib (0.35 mg/kg) + rituximab (10 mg/kg) once a week for 3 weeks (days 7, 14, 21), N = 7; FMD + bortezomib + rituximab: fasting + bortezomib (0.35 mg/kg once a week) + rituximab (10 mg/kg) once a week for 3 weeks (days 7, 14, 21), N = 7. Each treatment was administered for three cycles. Black arrows and higer magnifications indicate hematoxylin-positive lymphocytes. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice randomly allocated to ad libitum diet (CTRL, N = 18), cyclic FMD (N = 18), bortezomib + rituximab (N = 18), or cyclic FMD+ bortezomib + rituximab (N = 18) in an intravenous CLL murine model. Bortezomib was administered up to a maximum of 5 cycles. FMD and rituximab were administered until unacceptable toxicities or animal death/sacrifice.