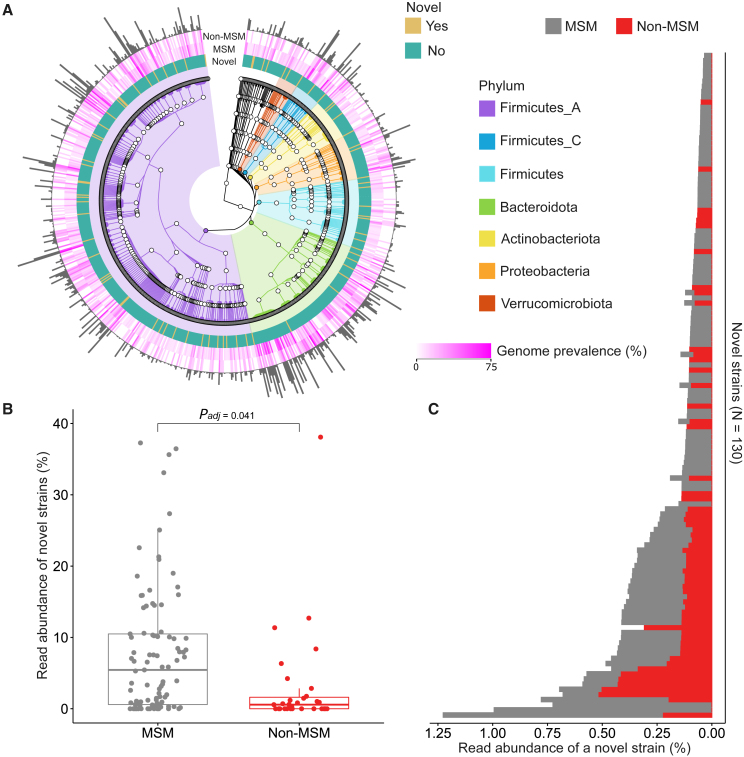
Figure 5.
Quantification of previously undescribed microbial species in the gut microbiome of MSM and non-MSM
(A) GTDB-Tk taxonomy structure of 765 species represented by 6,065 putative genomes reconstructed by de novo metagenomic assembly (only top seven phyla are highlighted in colors). The binary color of mustard and teal denote whether a species has been previously described or not, respectively. The gradient of magenta indicates the prevalence of species-assigned genomes in MSM and non-MSM (the color gradient was rescaled by arcsine-square root transformation for enhancing readability). Heights of the outmost histograms are in proportion to the number of genomes corresponding to the assigned species. Genome prevalence is defined as the number of species-assigned genomes divided by the number of individuals of MSM and non-MSM in percentage, respectively.
(B) The distribution of read abundance of previously undescribed strains in the metagenomic samples of MSM and non-MSM (adjusted by fixed-effect linear models,31 mean difference padj = 0.041).
(C) Read abundance stratified by strains, averaged over 93 MSM and 31 non-MSM, respectively. The read abundance of previously undescribed strains is defined as the percentage of reads mapped to previously undescribed strains to total reads in a metagenomic sample.
See also Table S5.