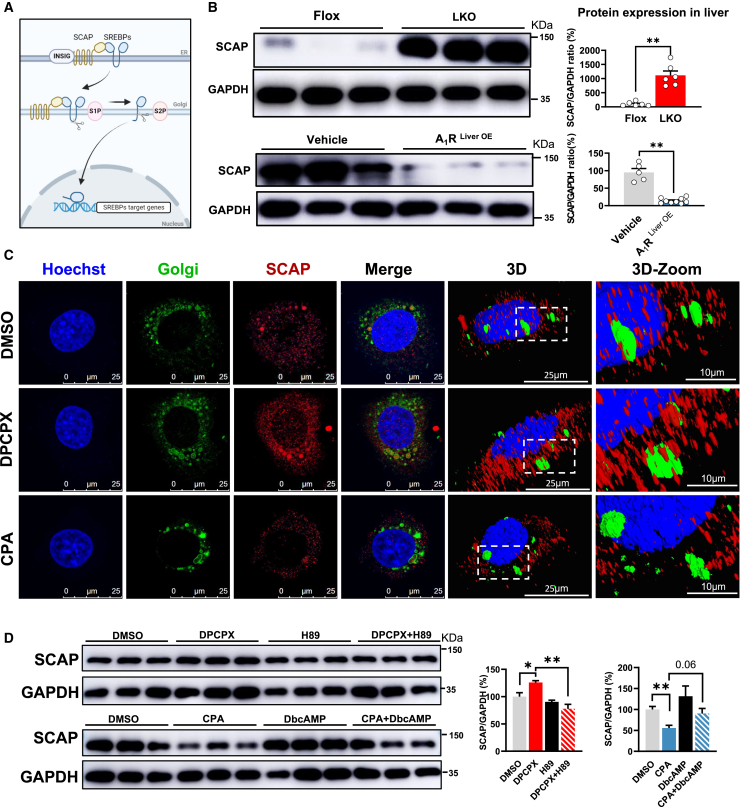
Figure 4.
A1R reduces the cellular content of SCAP and its anchoring at Golgi membrane
(A) Maturation process of SREBPs. SREBPs are exported from the ER to the Golgi apparatus by SCAP, and then transcriptional activation domain of SREBPs is released from the membrane by S1P and S2P. The released domain migrates into the nucleus and activates their transcription. Image created using BioRender.
(B) Protein expression of SCAP in the liver of A1RLiver OE or LKO mice.
(C) SCAP colocalizes with the Golgi apparatus. AML-12 cells were treated with DPCPX (1 μM) or CPA (1 μM) for 48 h. Fluorescent staining of nuclei (Hoechst, blue), Golgi (green), and SCAP (red) in each group was performed.
(D) Protein expression of SCAP in the AML-12 cells treated or co-treated with CPA and DbcAMP (200 μM, 12 h), or DPCPX and H89 (20 μM, 4 h). Results are representative of one biological replicate. Cell experiments performed n = 3. Data are depicted as mean ± SEM. Student’s unpaired t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.