Table 4.
Hydromonofluoroalkylation and hydroperfluoroalkylation of alkenes.
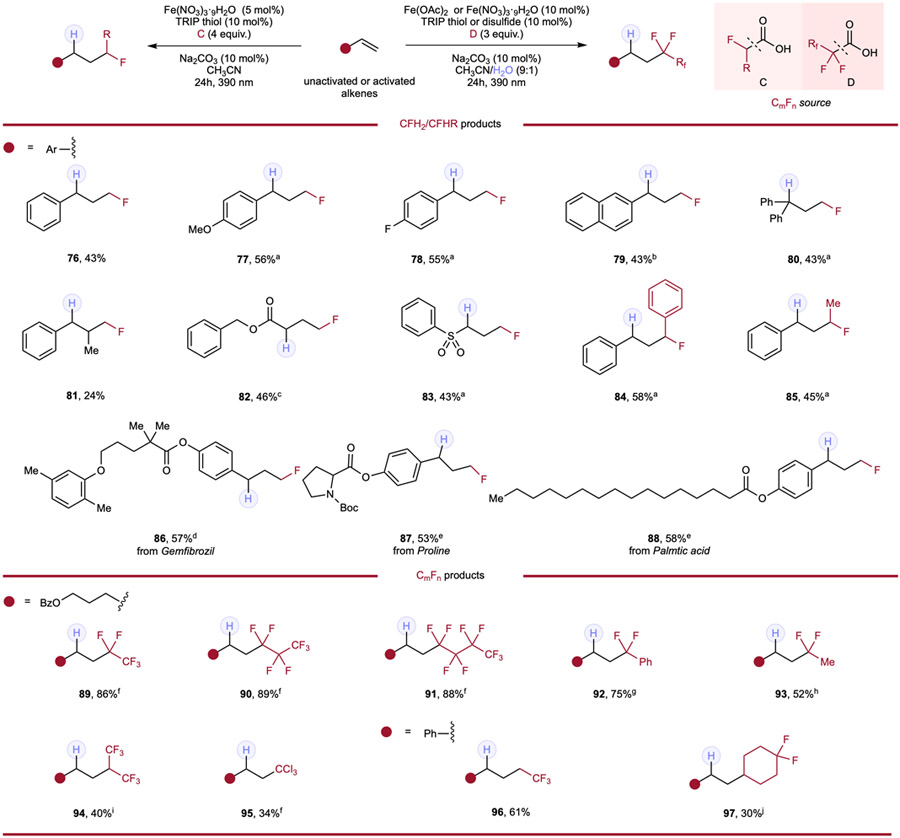
|
Reaction conditions of hydromonofluoromethylation: alkene (0.1mmol, 1.0 equiv.), monofluoroacetic acid (4.0 equiv.), Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (5 mol%), TRIP thiol (10 mol%), Na2CO3 (10 mol%) and CH3CN (0.1 M), 24h, RT, 390nm Kessil blue LED. a 0.2M. b With 10 mol% of H2O in 0.1M solution. c Without thiol. d With 10 mol% of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O in 0.2M solution. e With 10 mol% of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O. Reaction conditions of hydroperfluoroalkylation: alkene (0.1mmol, 1.0 equiv.), perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (3.0 equiv.), Fe(OAc)2 (10 mol%), HAT reagent (10 mol%), Na2CO3 (10 mol%) and CH3CN/H2O (9:1, 0.1 M), 24h, RT, 390nm Kessil blue LED. f With 10 mol% of TRIP thiol. g With 10 mol% of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O and 10 mol% of TRIP disulfide. h With 10 mol% of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O and 10 mol% of TRIP thiol. i With 10 mol% of TRIP disulfide. Reaction conditions of hydroalkylation of styrene: styrene (0.1mmol, 1.0 equiv.), carboxylic acid (4.0 equiv.), Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (5 mol%), TRIP thiol (5 mol%), Na2CO3 (10 mol%) and CH3CN (0.1 M), 24h, RT, 390nm Kessil blue LED. j 0.2M.
