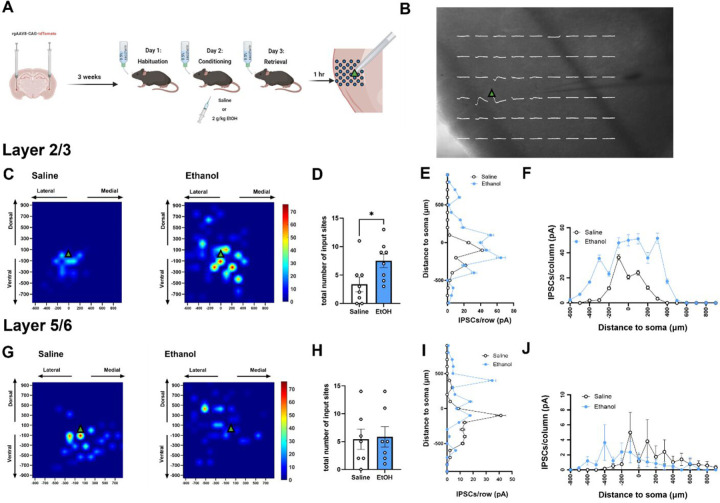
Figure 4. Local inhibitory input onto layer 2/3 IC-BLA projecting cells is greater following ethanol-CTA retrieval.
(A) Experimental design. Mice received bilateral intra-basolateral amygdala (BLA) injections of a retrograde AAV construct allowing for expression of fluorescent tdTomato in cells projecting from the anterior insula (IC) to the BLA prior to ethanol-CTA. 1 hr following ethanol-CTA retrieval, synaptic input maps to IC-BLA projecting cells were created using laser applied stimulation and uncaging. (B) Representative spatially localized uncaging-elicited events (white traces) are overlaid on a coronal section containing the IC. Green triangle indicates approximate location of cell soma in (B), (C), and (G). (C) Averaged input maps from IC-BLA layer 2/3 cells from saline-conditioned (left) or ethanol-conditioned mice (right). The number of total inhibitory input sites to layer 2/3 cells was greater in ethanol-conditioned mice relative to saline-conditioned controls (D). In layer 2/3, cumulative amplitude of uncaging-evoked events in pA in increments of 100µm from the soma across interlaminar (E) and intralaminar (F) extents was higher in ethanol-conditioned mice relative to saline-conditioned controls, particularly at locations nearest the soma, as indicated by significant main effects of distance and treatment, and a distance x treatment interaction. (G) Averaged input maps from IC-BLA layer 5/6 cells from saline-conditioned (left) or ethanol-conditioned mice (right). The number of total inhibitory input sites to layer 5/6 cells was not significantly different in ethanol-conditioned mice relative to saline-conditioned controls (H). In layer 5/6, cumulative amplitude of uncaging-evoked events in pA in increments of 100µm from the soma across the interlaminar extent (I) was impacted by a significant effect of distance, and a distance x treatment interaction such that saline-conditioned mice received stronger inhibitory inputs from ventral locations relative to ethanol-conditioned mice, and ethanol-conditioned mice received stronger inhibitory inputs from dorsal locations relative to saline-conditioned mice. Although there was no main effect of treatment nor an interaction, there was a significant main effect of distance along the interlaminar extent suggesting increased amplitude of uncaging-evoked events nearer to the cell body. (*p < 0.05, significant effect of ethanol).