Figure 2.
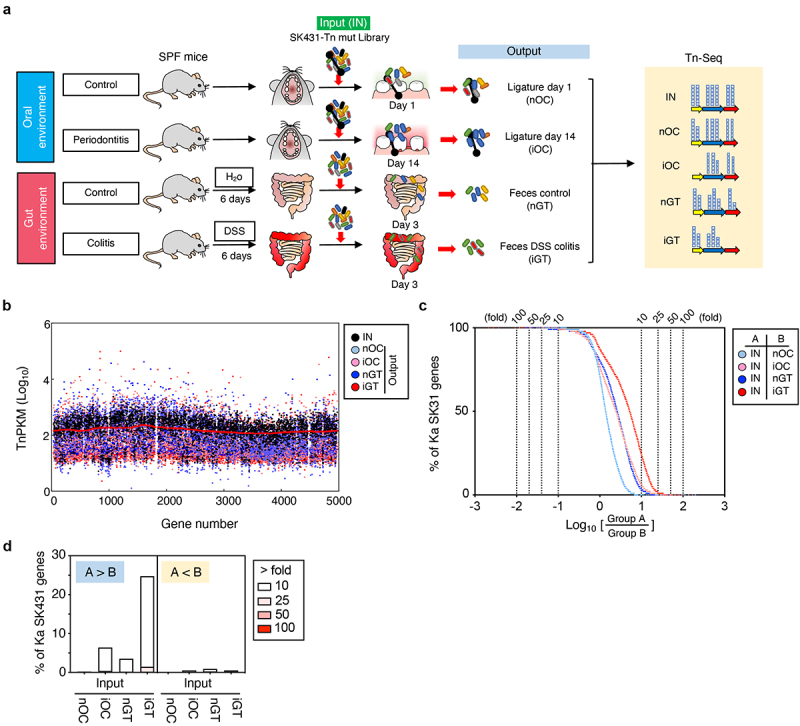
Experimental design and overview of genes required for the colonization in the steady state and the inflamed oral and gut mucosae. (a) A transposon (tn) mutant (mut) library of Ka SK431 was inoculated into specific pathogen-free (SPF) C57BL/6 mice by soaked ligature and orogastric gavage for the oral and gut sites, respectively (input: IN). Ligature and feces were collected from the healthy control mice and the inflamed (periodontitis or colitis) mice on indicated days after inoculation (output). DNA was isolated from the input and output samples and sequenced by Illumina NovaSeq. The resulting reads were mapped to the Ka SK431 genome, and the abundance of reads at each insertion site from all output samples were compared to those for the input samples to determine a fold-change value for each gene. (b) Genome-wide distribution and frequency of mutations in the library. Individual tn densities per kilobase gene per million reads (TnPKM) are shown as dots on the map of Ka KCTC2190 complete genome, instead of incomplete SK431 genome. Red line, 3,000 gene moving average of IN. (c) Number of genes that were required for the colonization in the indicated locations and conditions. The log ratio of the average TnPKM of indicated group a per group B for individual genes is shown on the X-axis. The accumulation curves of the number of the gene from the top (rich in group B) to the bottom (rich in group A) are shown on the Y-axis. (d) Graph summarizing the results of (C).
