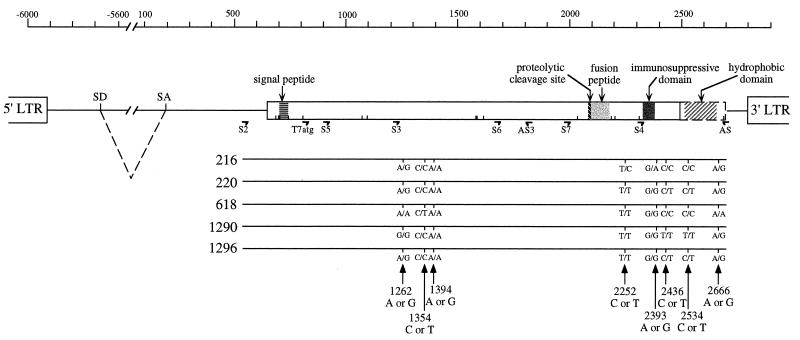
FIG. 1.
Identification of polymorphic sites within the sequences of ERV-3 envelope genes from five unrelated individuals. The ERV-3 provirus with the envelope open reading frame (open rectangle) and its expected functional domains, including the proteolytic cleavage site, the fusion peptide, and the immunosuppressive domain, are schematically represented at the top. The putative hydrophobic domain is shown in a dotted rectangle as an extension of the open reading frame if the stop codon at nucleotide 2500 is read through. The G insertion at position 796 (see Table 1) leads to an upstream shift in the frame, unlike that of the previously published ERV-3 sequence, and introduces a potential signal peptide and four new Met codons (represented by short vertical lines). LTR, long terminal repeat; SD, splice donor site; SA, splice acceptor site. The primers used in this study are indicated, and 5′-3′ sequences are given for S2 (CGGCCGAAGCTTGAGTCATCATCAGGG), T7atg (GCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGAACAGACCACCatgACTAAAACCCTGTTGTATCA), S3 (AACCAACAATCACTAGGGCC), AS3 (TGCCCCTCCATAAAGTCTTTCCTAG), and AS (GTTAATACTTAGTTAGGGCC). At the bottom, the envelope gene sequences of five individuals and the corresponding polymorphic sites within the ERV-3 consensus sequence are represented; both alleles for each site are indicated. Numbers refer to the ERV-3 pol-env published sequence (4; accession no. M12140).