Fig. 3.
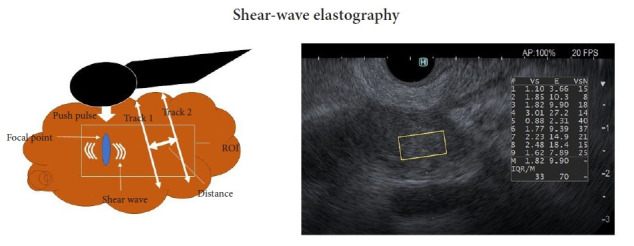
Principle of EUS shear-wave measurement and a EUS-SWE monitor image. Acoustic radiation force (push pulse) is sent to the pertinent point of the region of interest (ROI), and the push pulse generates a shear wave at the edge. The shear-wave velocity (distance/arrival time lag [Vs, m/s]) between two search points is calculated with a track pulse. If the tissue is harder, the shear wave propagates faster. EUS, endoscopic ultrasonography; EUS-SWE, EUS shear-wave elastography; Vs, shear-wave velocity; E = 3(Vs2ρ) (ρ is the tissue density); VsN, the percentage of the net amount of effective shear-wave velocity.
