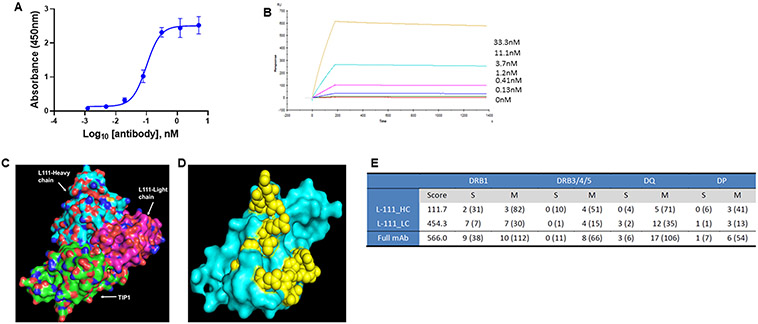
Figure 2. Binding of L111 antibody to the TIP1 protein.
A. ELISA assay for the binding of L111 antibody to recombinant TIP1 protein. TIP1 protein was coated on ELISA plates. Four-fold serial dilutions (starting at 5 nM) of the purified L111 antibodies were incubated with the protein. Anti-human HRP conjugated antibody was used as the detection antibody along with TMB substrate. Absorbance at 450 nm vs. concentration is plotted in the graph. The data were fitted using the log (agonist) vs. response -- Variable slope (four parameters) model in GraphPad Prism software. B. Recombinant TIP1 protein (ligand) was immobilized on the surface of the CM5 sensor chip. The reference surface was prepared and blocked. Various concentrations of L111 antibodies (as indicated) were passed over the ligand. Reference subtracted sensograms were fitted using the BIAevaluation software, and on-rates, off-rates, and KD were calculated. C. Computational docking of TIP1 with L111 antibody was performed using the Schrodinger software package. The L111 antibody heavy chain (cyan) and light chain (magenta) are shown to interact with the TIP1 protein (green). D. The 3D surface model of TIP1 shows the predicted interacting residues with the L111 antibody in yellow spheres. E. Immunogenicity assessment of L111 antibody. The table shows DRB1 scores and epitope counts per gene family and per binding strength class. Numbers in brackets refer to TCR-filtered and self-peptides.