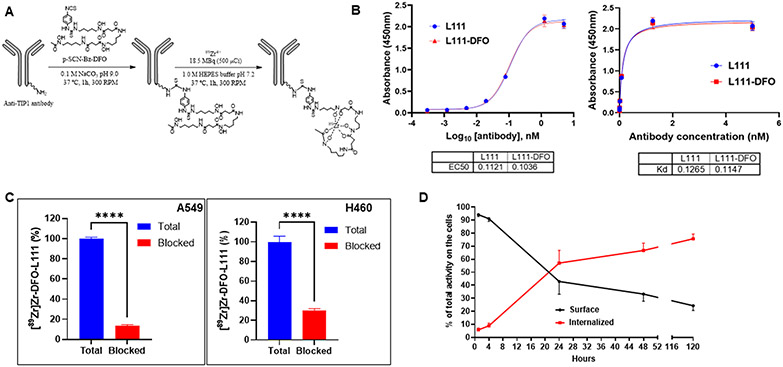
Figure 4. Conjugation of desferoxamine to L111 antibody, radiolabeling, and its characterization.
A. Labeling scheme for the L111 antibody with [89Zr]Zr. The L111 antibody was buffer exchanged (Chelex-treated 0.1 M sodium carbonate/bicarbonate, pH 9.0). DFO was added, and the mixture was allowed to react for 1 h at 37 °C. The reaction mix was buffer exchanged to 1.0 M HEPES buffer. [89Zr]Zr-oxalate was neutralized to ~pH 7.0–7.4 using 1.0 M HEPES pH 7.2 and subsequently mixed with DFO–L111 Ab samples. The reaction mixture was incubated for 60 min at 37 °C at 300 rpm. B. ELISA for binding of DFO-L111 to TIP1 protein. Four-fold serial dilutions of the L111 antibodies were incubated with TIP1 protein for indirect ELISA assay. The ELISA data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software and fitting using log (agonist) vs. response -- Variable slope (four parameters) One Site -- Specific binding. The tables below the graph show the EC50 and Kd values, respectively. C. TIP1-specific cell binding of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-L111 was blocked by excess cold L111 (red bars). Bars are mean ± S.D. of % bound activity from triplicate samples per group. ****P <0.001. D. Evaluation of cell surface vs. internalized radiolabeled L111 antibody.