Figure 8:
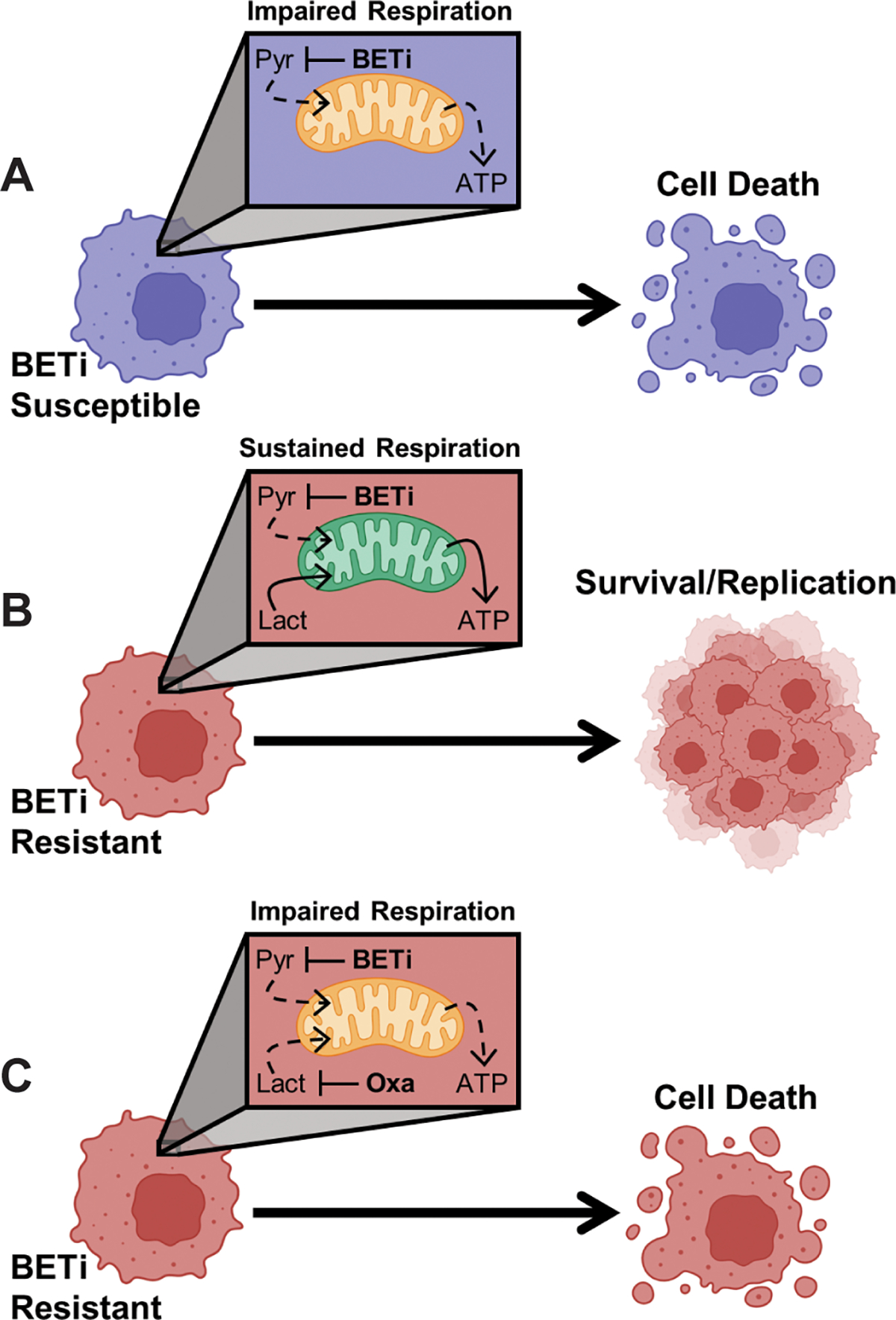
AML myeloblasts utilize lactate as a metabolic bypass to resist BET inhibition. (A) Treatment with BETi disrupts glycolysis resulting in a collapse in intracellular pyruvate (Pyr) and an inability to maintain mitochondrial respiration resulting in cell death. (B) BETi resistance coincides with an increased capacity for mitochondria to utilize lactate (Lact) as an alternative carbon source to sustain mitochondrial respiration. (C) However, co-treatment with BETi and oxamate (Oxa) to prevent utilization of lactate impairs mitochondrial respiration in BETi-resistant cells leading to cell death. Created with BioRender.com.
