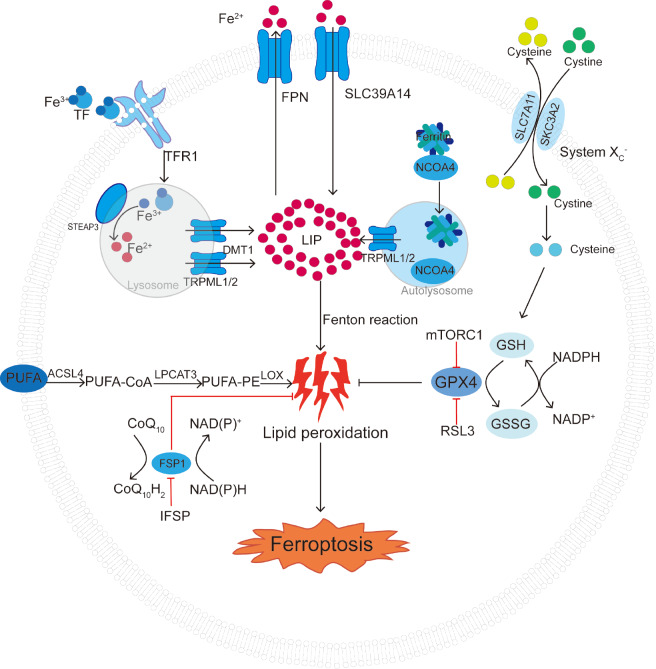
Figure 1 .
Basic mechanisms and regulatory pathways of ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is related to intracellular free Fe2+ metabolism disorders or dysfunction of glutathione peroxidation and polyunsaturated fatty acid lipid peroxidation. This figure illustrates the basic process of ferroptosis and shows the inducers and inhibitors of related processes. The black arrows and red blunt lines represent the promotion and inhibition of ferroptosis, respectively. TF, transferrin; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; DMT1, divalent metal ion transporter 1; TRPML1/2, mucolipin TRP channel 1/2; FPN, ferroportin; SLC39A14, metal transporter protein; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; LIP, labile iron pool; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase 4; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; LOX, lysyl oxidase; IFSP, inhibitor ferroptosis suppressor protein; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; CoQ10H2, ubiquinol; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.