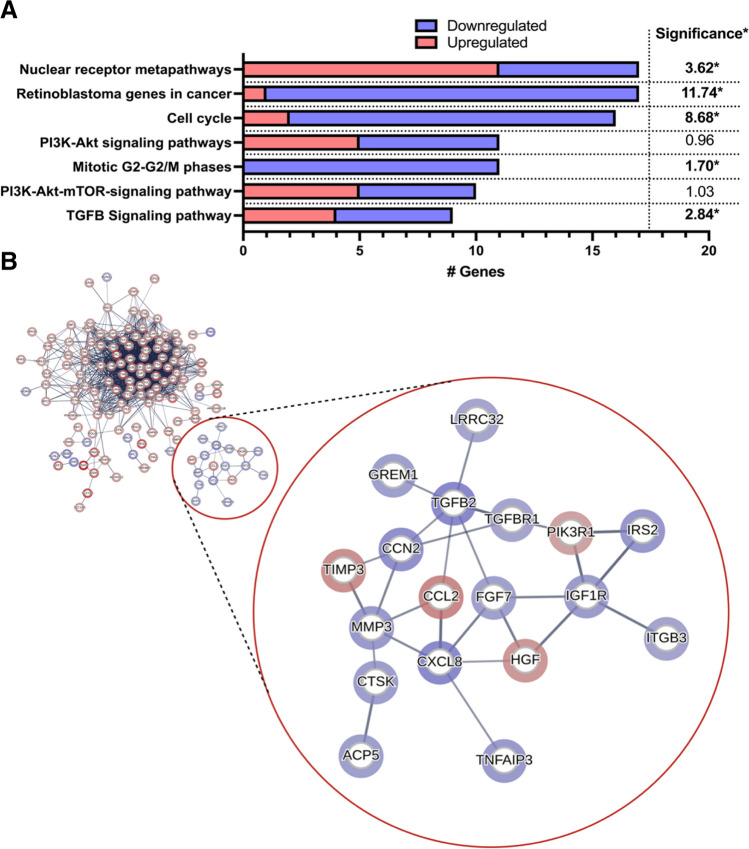
Fig. 4.
A A functional gene enrichment analysis reveals that rapamycin treatment elicits significant differential gene expression within specific pathways (using WIkiPathways tool in Transcriptome Analysis Console) involved in cancer, cell cycle, and PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling. Of importance, the TGF-β signaling pathway was significantly enriched. The number of genes enriched within each pathway is the x-axis, where blue are downregulated genes, and red are upregulated genes. On the right-most side, the significance (-log10(p-value)) is presented for each enriched pathway. * denotes significance (p < 0.05). B A total of 316 genes with 2-fold differential expression and FDR-adjusted p-value of less than 0.05 were input into STRING to acquire protein-protein interactions (PPIs). A gene enrichment map was constructed from genes with a 2-fold or greater change in expression between rapamycin and DMSO groups using the STRING database. Panel B focused on a group of 18 protein-protein interactions that are unconnected to the larger group of interactions, which involves cytokine (IL-8), TGF-β2, and PI3K-Akt signaling. Nodes represent proteins encoded by their labelled gene locus. Edges represent protein-protein associations of high confidence (0.7). Halo color and intensity signifies gene down-regulation (red) or up-regulation (blue) and fold-change value, respectively. The nodes correspond to the gene/proteins and the edges represent the interactions. After network analysis and removing unconnected nodes, 310 nodes were identified