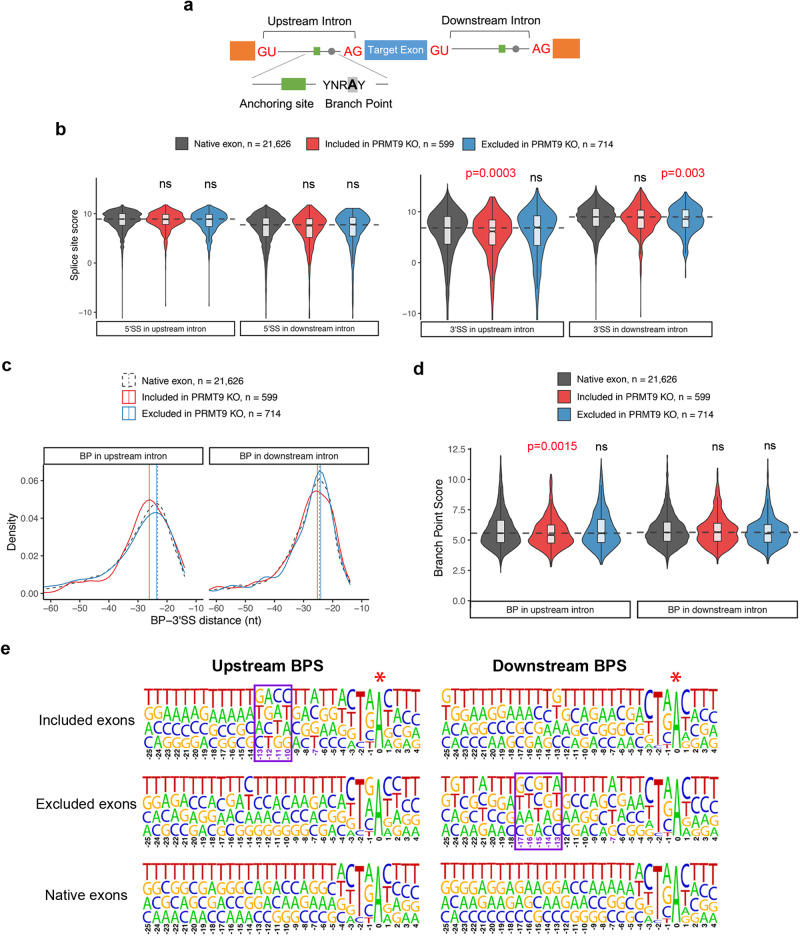
Fig. 6. PRMT9-regulated splicing targets exhibit nonconsensus anchoring site sequences.
a A schematic illustration of splicing cis-regulatory elements located in the intron sequence of pre-mRNA. Branch point and anchoring site locations are highlighted in gray and green, respectively. b Violin plot demonstration of the maximum entropy score of the 5' and 3' splice sites in upstream or downstream introns of differentially spliced cassette exons. The middle line of the boxplot represents median value. The low and high ends of the box represent the 25% and 75% quantiles, respectively. The two whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range. The statistical significance against background native cassette exons was assessed using a two-sided Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test. ns, not significant. c Density plot of the relative positions of predicted branch point (BP) locations distanced from their corresponding 3' splice sites. Native exon, n = 21,626; Included in PRMT9 KO, n = 599; Excluded in PRMT9 KO, n = 714. d Violin plot demonstration of BP scores from predicted branch point sites. The middle line of the boxplot represents median value. The low and high ends of the box represent the 25% and 75% quantiles, respectively. The two whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range. The statistical significance against background native cassette exons was assessed using a two-sided Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test. ns, not significant. Native exon, n = 21,626; Included in PRMT9 KO, n = 599; Excluded in PRMT9 KO, n = 714. e Sequence logo demonstration of the nucleotide frequency upstream of the predicted branch point sites. The height of the symbols within the stack indicates the observed frequency of the corresponding nucleotide at that position. The 0 point marks the position of the branch point adenosine (marked with an asterisk). Sequences from −25 nt to 4 nt relative to the branch point were shown, which include the reported anchoring site sequence covering 6 to 25 nt upstream of the branch point. The boxes highlight the sequence variations in PRMT9-regulated alternatively spliced exons in comparison to all native exons.