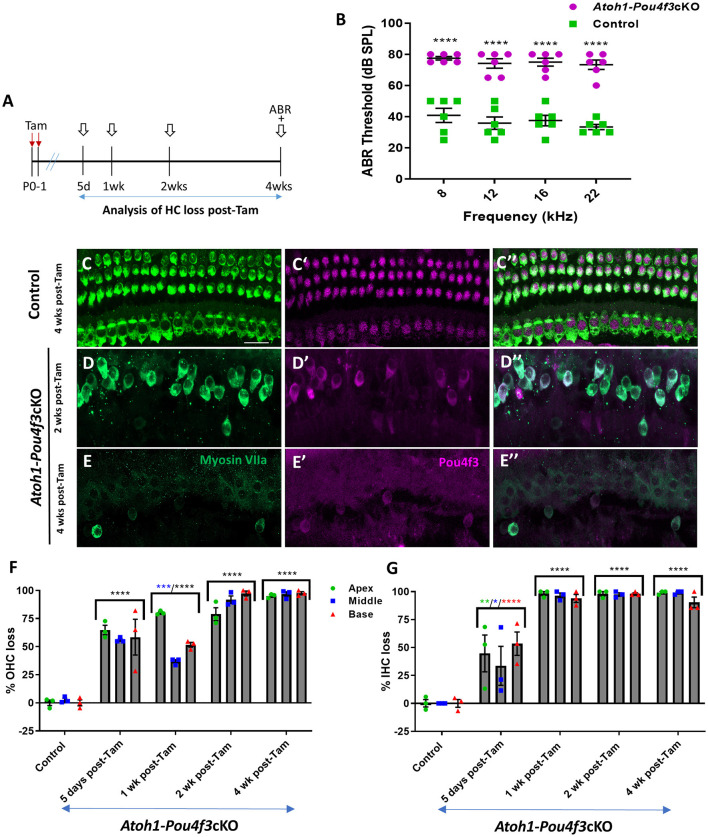
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic for the experimental design using Atoh1-Pou4f3cKO mice to delete Pou4f3 from both IHCs and OHCs at P0–P1. Open arrows indicate post-tamoxifen (post-Tam) timepoints when HC loss was assessed. (B) At 4 weeks after Pou4f3 deletion, there was a significant elevation in ABR thresholds in Atoh1-Pou4f3cKO mice compared to their control littermates at all frequencies tested [N = 6; significant main effect of genotype, F(1,40) = 302.8, p < 0.0001]. Asterisks indicate comparisons between genotypes at each frequency based on a Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc test. (C–E″) Representative confocal images from control (C–C″) and Atoh1-Pou4f3cKO (D–E″) cochleae. HCs in the control cochleae remained intact (myosin VIIa, green) and had nuclear expression of POU4F3 (magenta). However, many HCs were missing in Atoh1-Pou4f3cKO cochleae at 2 and 4 weeks after Pou4f3 deletion and most of the remaining HCs exhibited POU4F3 immunoreactivity in their cytoplasm. Quantification of OHC (F) and IHC (G) loss in control and Atoh1-Pou4f3cKO cochleae (N = 3) between 5 days and 4 weeks post-Tam. For OHCs there was a significant main effect of time [F(4,10) = 142.2, p < 0.0001] and interaction between time and cochlear turn [F(8,20) = 6.697, p = 0.0003]. For IHCs there was a significant main effect of time [F(4,10) = 56.95, p < 0.0001]. In (F) and (G), differences from control within each cochlear turn are indicated by the asterisks based on a Tukey's-corrected post-hoc test. Green asterisks are p values for the apical turn, blue asterisks are p values for the middle turn, and red asterisks are p values for the basal turn. Black asterisks were used when the p value was the same for two or three turns. Comparisons across time post-Tam and across cochlear turns within the same genotype are presented in Supplementary Tables 2A,B. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar = 20 μm. Pou4f3 deletion from immature HCs at birth causes elevated ABR thresholds and progressive HC loss.