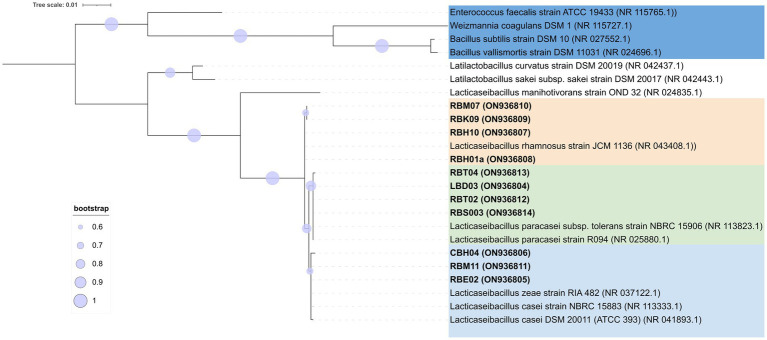
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the relationships among non-starter lactic acid bacteria (NSLAB) strains isolated from PR cheeses at 12, 18, 24, and 30 months of ripening. The tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood method and the Kimura’s two-parameter model (Kimura, 1980) in Mega X software. Representative isolates for each sample are shown in bold, with the sequence accession numbers indicated in brackets. Sequence data for reference strains were from the NCBI RefSeq database. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites. The final dataset involved 24 nucleotide sequences for a total of 1,372 positions. Bootstrap values (>60%) are indicated at branch points based on 1,000 replications. The tree is rooted using the branch leading to four outgroup species (W. coagulans, B. subtilis, B. vallismortis, and E. faecalis). The tree is drawn in scale with branch length measured in the number of substitutions per site: bar, 0.01 substitutions per nucleotide position. The outgroup species are highlighted in the blue background, Lcb. rhamnosus in orange background, Lcb. casei/Lcb. zeae in green background, and Lcb. paracasei in light blue background, respectively. The tree was visualized with ITOL (Letunic and Bork, 2019).