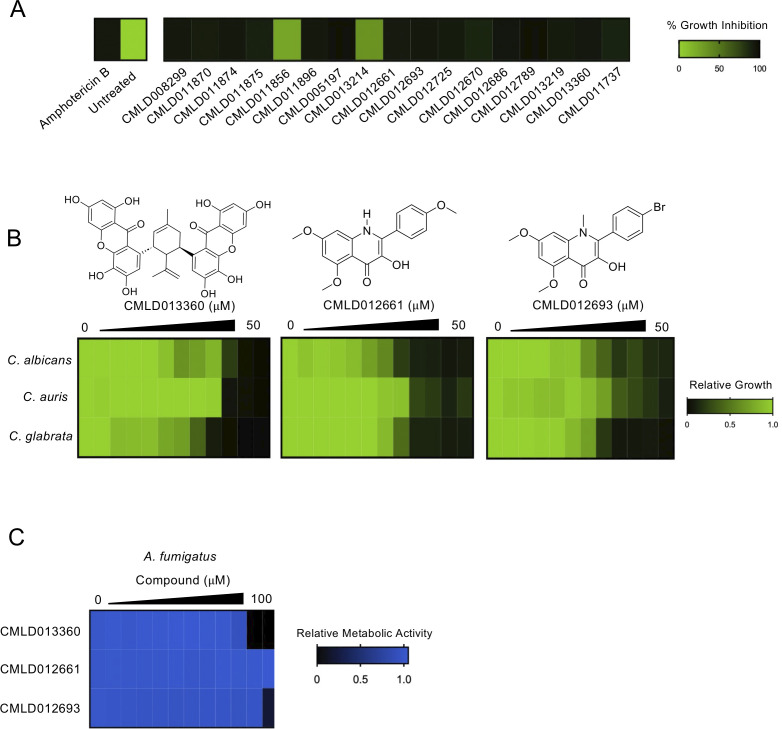
Fig 1.
Screening of the BU-CMD chemical library identifies compounds with activity against a clinical isolate of C. albicans. (A) C. albicans (DPL15, a caspofungin-resistant isolate) was grown in RPMI for 48 hours at 30°C with or without compounds (25 µM) from the BU-CMD library. Relative growth was measured by OD600. Compounds were considered hits if they reduced growth >80% relative to the median growth observed in the screen. Hit compounds were tested a second time to confirm bioactivity. Growth was normalized and then calculated as a percentage of compound-free controls (see color bar). (B) Dose-response assays were performed in a 384-well plate format in technical duplicate, with two-fold dilution gradients of the three prioritized compounds against diverse fungal pathogens. Relative growth was measured by absorbance at 600 nm (OD600) after a 48-hour incubation at 30°C in RPMI (see color bar). Data plotted represent results from one of two biological replicates that yielded similar results. (C) Dose-response assay was performed as described in (B). Standard dye reduction (Alamar blue) assay was used to measure the relative viable Aspergillus fumigatus cell number (see color bar). Data plotted represent results from one of two biological replicates that yielded similar results.