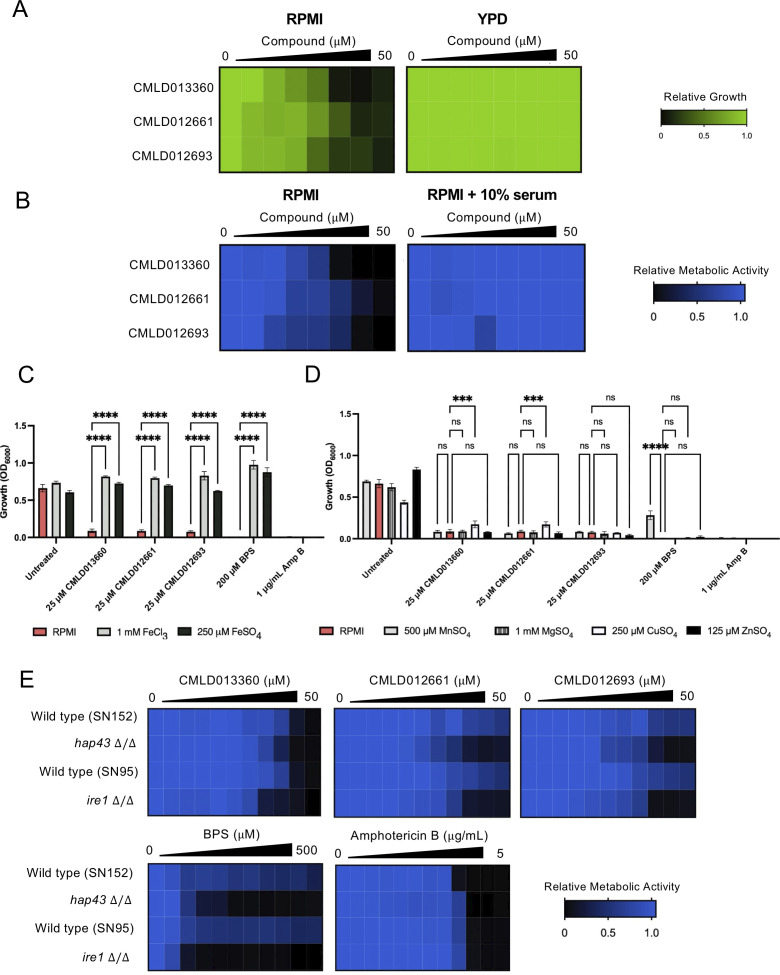
Fig 2.
CMLD12661, CMLD012693, and CMLD013360 inhibit C. albicans growth through iron chelation. (A) Dose-response assays of three prioritized compounds in RPMI and YPD in a 96-well plate format. Relative cell growth was assessed by absorbance at 600 nm (OD600) after 48-hour incubation at 30°C (see color bar). (B) Dose-response assays of three prioritized compounds in RPMI and RPMI + 10% serum in 96-well plates. After a 48-hour incubation at 30°C, relative metabolic activity was assessed by standard dye reduction (Alamar blue) assay (see color bar). (C) Supplementing media with additional iron salt (FeSO4 or FeCl3) restores fungal growth in the presence of CMLD compounds and the classical metal chelator, BPS (bathophenanthrolinedisulfonic acid). The activity of the known antifungal, amphotericin B (Amp B), was not influenced by iron supplementation. Mutant strains and their respective wild-type parental controls were grown overnight in YPD and then sub-cultured into RPMI supplemented with a concentration of the indicated compound that inhibited growth by 80% in RPMI medium alone. RPMI was also supplemented with 250 µM FeSO4 or 1 mM FeCl3, as indicated. Relative cell growth was assessed by absorbance at 600 nm (OD600) after 48-hour incubation at 30°C. Bars represent the mean of technical triplicates, and error bars represent ±SD (standard deviation) of technical triplicates, ****P ≤ 0.0001. (D) Supplementing media with metal salts (MnSO4, MgSO4, CuSO4, and ZnSO4) has no to minimal impact on the antifungal activity of compounds. Assay was performed as described in (C). Bars represent the mean of technical triplicates, and error bars represent ±SD of technical triplicates, ****P ≤ 0.0001, and ***P ≤ 0.001. Data plotted represent results from one of two biological replicates that yielded similar results. (E) Deletion of IRE1 or HAP43 increases the bioactivity of CMLD013360, CMLD012661, and CMLD012693 against C. albicans. Parental wild-type strains, and ire1Δ/ire1Δ and hap43Δ/hap43Δ mutant strains, were grown overnight in YPD and then subjected to dose-response assays in RPMI medium with two-fold dilution gradients of CMLD013360, CMLD012661, and CMLD012693. BPS, a metal chelator, was included as a positive control. Relative cell growth was assessed by a standard dye reduction (Alamar blue) assay after 48-hour incubation at 30°C. For all dose-response assays, growth was averaged between technical duplicates and normalized to drug-free control wells. Heat maps plotted are representative of two biological replicates.