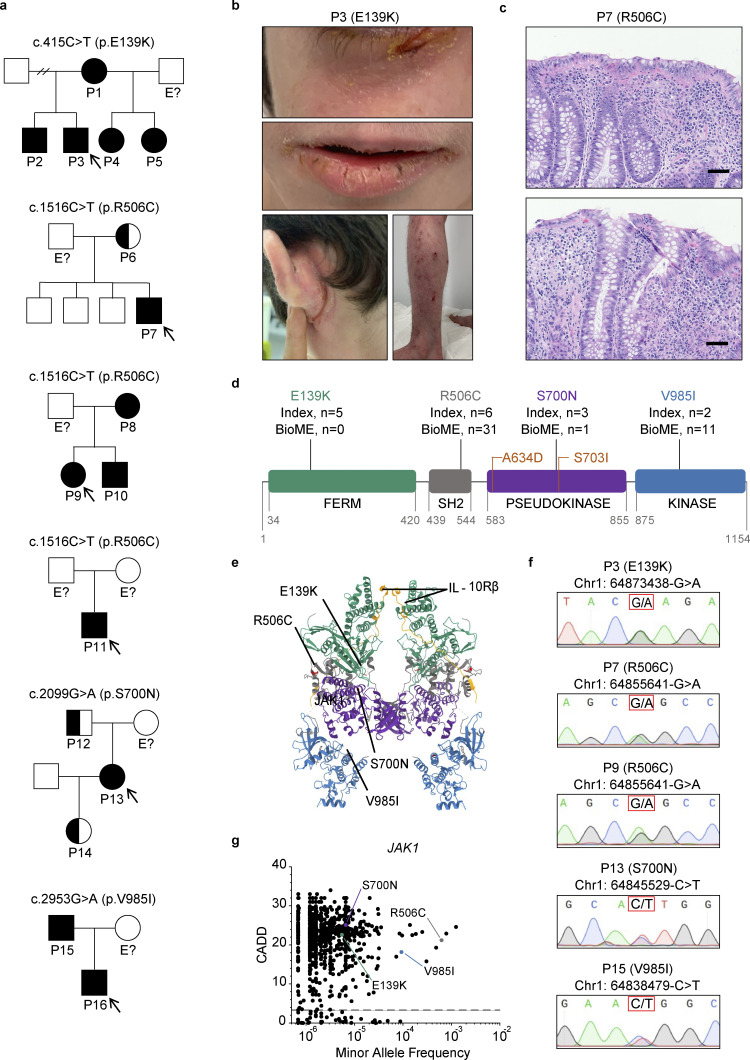
Figure 1.
Six families with inflammatory and autoimmune diseases are found to harbor heterozygous JAK1 variants affecting all four JAK1 protein domains. (a) Pedigrees for each kindred with the identified JAK1 variants. Affected individuals (shaded) or unaffected carriers (half-shaded) are numbered (P#). Unshaded individuals labeled with “E?” have an unknown JAK1 genotype status. All other unshaded individuals are JAK1 WT. Initially presenting probands are identified by arrows. Male sex is indicated by squares and female sex by circles. (b) Severe atopic dermatitis (SCORAD = 60) affecting P3. Upper panel represents affected areas underneath the eyes. Middle panel represents affected areas of the lower face. Lower left panel represents affected areas of the lower extremities and feet. Lower right panel represents affected areas of the upper extremities and hands. (c) H&E-stained tissue sections of small intestine from P7 (JAK1 R506C) depicting focal neutrophilic inflammation (upper and lower), granuloma (upper), and cryptitis (lower). 100× magnification. Representative micrographs shown from six individual images. Black scale bars are equivalent to 100 μm. (d) Location of four amino acid substitutions arising from the identified JAK1 SNVs along the four domains of the JAK1 protein. Counts of subjects from index families (Index) and subjects present in the Mount Sinai Biobank. Previously described GoF variants are indicated in orange. Digits below domains represent amino acid numbers bordering each domain. (e) Full crystal structure of murine JAK1 dimer, colored by domain, complexed with intracellular tails of IFN-λR1/IL-10Rb in yellow (PDB ID 7T6F) (Glassman et al., 2022). Domains colored as follows: FERM = green, SH2 = gray, pseudokinase = purple, kinase = blue. Corresponding murine-to-human amino acid substitutions depicted in red and labeled by protein consequence. (f) Chromatograms from Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA sampled from affected individuals. Corresponding genomic locations and nucleotide substitutions are indicated above each chromatogram. P11 and P16 did not provide a biological sample and are therefore not included in the data set. (g) Minor allele frequencies for missense JAK1 variants present in gnomAD (v4.0) mapped against corresponding CADD scores (99% confidence interval, HGMD). Prototype JAK1 variants are labeled for reference. The dotted line represents JAK1 mutation significance cutoff (MSC) of 3.313.