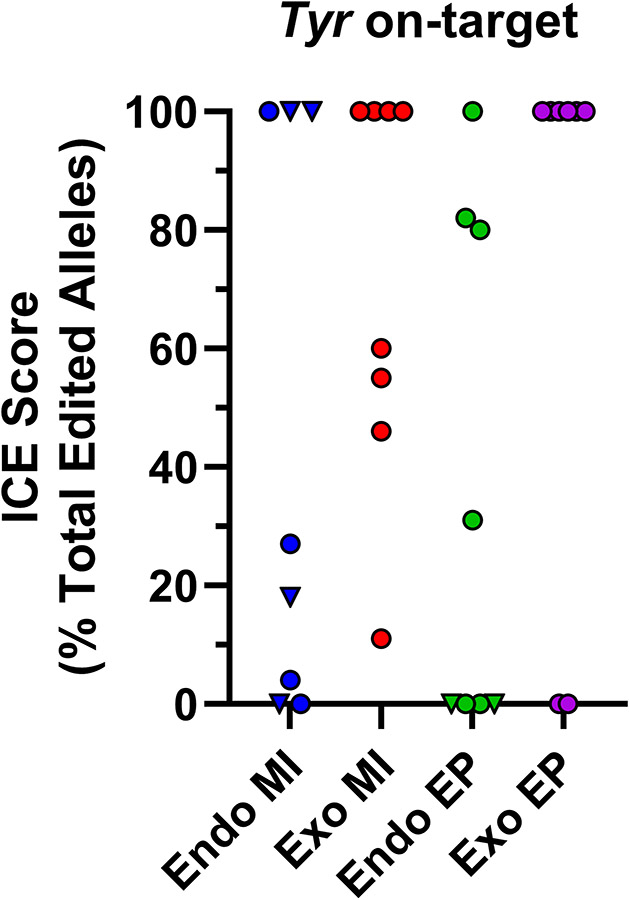
Figure 5.
Off-target genome editing occurs with both endogenous and exogenous Cas9. Zygotes were generated from wild-type and Hprt1Gdf9-Cas9 females and microinjected or electroporated with or without exogenous Cas9, respectively, and two gRNAs targeting Tyr (N=8 animals or blastocysts per Cas9 source/route of administration). Sanger sequencing and ICE analysis of sequencing traces were performed to detect genome editing at the on-target and top 4 predicted off-target sites for each gRNA and to calculate indel allele contribution. (A) Scatter plot of ICE score for each Cas9 source/route of administration for the Tyr on-target site. Endogenous MI and EP samples with inheritance of the Hprt1Gdf9-Cas9 transgene are displayed as triangles, all other samples are circles. (B) Scatter plot of ICE score for each Cas9 source/route of administration for one off-target site. Of the 8 off-target loci screened for the 2 gRNAs employed (4 per guide), mutagenesis was detected at only this off-target site. Of the 2 mice with an off-target event from the Endogenous MI samples, one had inheritance of the Hprt1Gdf9-Cas9 transgene (triangle). (C) Scatter plot depicting off-target ICE score versus on-target score for the only off-target site with identified mutagenesis events to illustrate occurrence of on- and off-target events occurring within the same sample. Endo, endogenous Cas9; Exo, exogenous Cas9; MI, microinjection; EP, electroporation; (T), Hprt1Gdf9-Cas9 transgenic.