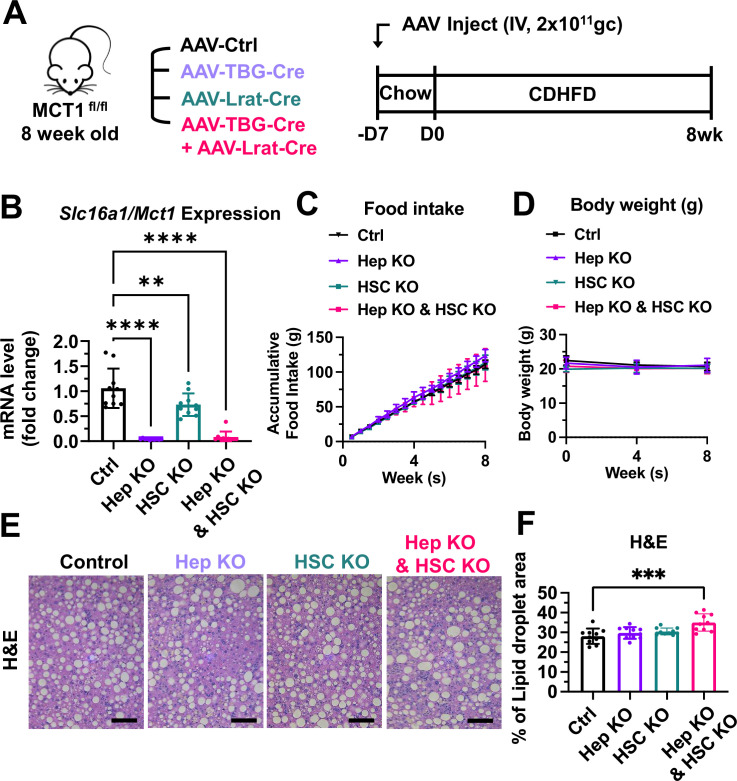
Figure 6. MCT1 depletion did not resolve steatosis in the choline-deficient, high-fat diet (CDHFD)-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) model.
(A) Male MCT1fl/fl mice (8 weeks, n=10) were intravenously injected with 2×1011 gc of AAV-TBG-Cre or AAV-Lrat-Cre or both. The same amount of AAV-TBG-null or AAV-Lrat-null was used as a control. A week after the injection, mice were fed a CDHFD for 8 weeks and sacrificed. (B) Slc16a1/Mct1 mRNA expression levels in whole livers were examined. (C) Food intake and (D) body weights were monitored. (E) CDHFD-induced steatosis was monitored by H&E (scale bar: 200 µm). (F) % of lipid droplet areas was quantified (mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001, ****: p<0.0001).