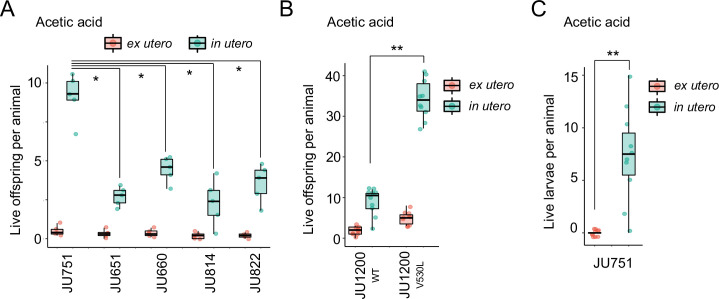
Figure 14. Differences in survival of eggs developing ex utero versus in utero when exposed to environmental stress.
(A) Differences in survival of eggs developing ex utero versus in utero when exposed to acetic acid (10 M, 15-min exposure). Comparison of the strain JU751 (Class IIIB, strong retention) to four strains (Class II, canonical retention) isolated from the same locality. Examining only data for eggs exposed in utero, JU751 exhibited a significantly higher number of surviving offspring compared to all other strains (ANOVA, effect Strain: F4,20=15.96, p<0.0001; Tukey’s honestly significant difference, all p<0.05). N=5 replicates per genotype and treatment (10 hermaphrodites at mid-L4 +30 hr per replicate). See Figure 14—figure supplement 1 for additional (control) data of the experiment. (B) Comparing the Class II strain JU1200WT (canonical retention) and the JU1200KCNL-1 V530L strain (strong retention): differences in the number of surviving eggs ex utero (extracted by dissection) versus in utero (eggs retained in mothers) exposed to a high concentration of acetic acid (10 M, 15-min exposure). JU1200KCNL-1 V530L exhibited a significantly higher number of surviving offspring in utero when exposed to acetic acid compared to JU1200WT (Kruskal-Wallis Test, χ2=14.35, df=1, p=0.0002). N=10 replicates per genotype per treatment. (C) Differences in the number of surviving internally hatched larvae exposed to acetic acid (10 M, 15-min exposure) using the strain JU1200KCNL-1 V530L: ex utero (extracted by dissection) versus in utero (larvae retained in mothers). The number of live larvae per mother was significantly higher in utero compared to ex utero (Kruskal-Wallis Test, χ2=13.89, df=1, p=0.0002). N=10 replicates per genotype per treatment.
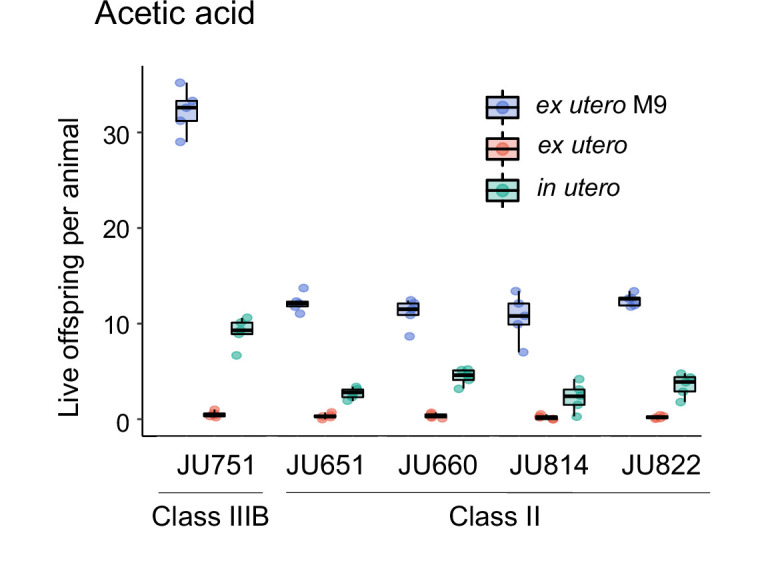
Figure 14—figure supplement 1. Additional data for the experiment shown in Figure 14A.